Serum Sulfhydryl Groups, Malondialdehyde, Uric Acid, and Bilirubin as Predictors of Adverse Outcome in Heart Failure Patients due to Ischemic or Nonischemic Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 33936385
- PMCID: PMC8062185
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6693405
Serum Sulfhydryl Groups, Malondialdehyde, Uric Acid, and Bilirubin as Predictors of Adverse Outcome in Heart Failure Patients due to Ischemic or Nonischemic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of heart failure (HF). The aim of the study was to investigate the prognostic value of oxidation-reduction (redox) markers in patients with HF due to ischemic and nonischemic cardiomyopathy. The study included 707 patients of HF allocated into two groups depending on ethology: ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) (n = 435) and nonischemic cardiomyopathy (nICM) (n = 272), who were followed up for one year. The endpoint occurrence (mortality or heart transplantation) in a 1-year follow-up was similar in the ICM and nICM group. The predictive value of endpoint occurrence of oxidative stress biomarkers such as the serum protein sulfhydryl groups (PSH), malondialdehyde (MDA), uric acid (UA), bilirubin, and MDA/PSH ratio and other clinical and laboratory data were assessed in both groups (ICM and nICM) separately using univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses. In multivariate analysis, the higher concentrations of UA (p = 0.015, HR = 1.024, 95% CI (1.005-1.044)) and MDA (p = 0.004, HR = 2.202, 95% CI (1.296-3.741)) were significantly associated with adverse prognosis in patients with ICM. Contrastingly, in patients with nICM, we observed that higher bilirubin concentration (p = 0.026, HR = 1.034, 95% CI (1.004-1.064)) and MDA/PSH ratio (p = 0.034, HR = 3.360, 95% CI (1.096-10.302)) were significantly associated with increased risk of death or HT. The results showed the association of different oxidative biomarkers on the unfavorable course of heart failure depending on etiology.
Copyright © 2021 Celina Wojciechowska et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
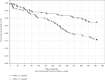
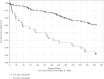
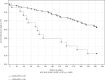
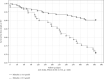
Similar articles
-
Malondialdehyde and Uric Acid as Predictors of Adverse Outcome in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Oct 9;2019:9246138. doi: 10.1155/2019/9246138. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31687090 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Oxidative Stress Parameters in Heart Failure Patients Depending on Ischaemic or Nonischaemic Aetiology.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Sep 17;2019:7156038. doi: 10.1155/2019/7156038. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31636808 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Outcomes in Ischemic vs Nonischemic Cardiomyopathy in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: A Report From the GARFIELD-AF Registry.JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Jun 1;4(6):526-548. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.4729. JAMA Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31066873 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the Clinical Outcome of Ischemic and Nonischemic Cardiomyopathy in Heart Failure With Concomitant Opioid Use Disorder.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023 May;48(5):101609. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.101609. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36690309 Review.
-
Prognostic Value of Late Gadolinium Enhancement in Predicting Life-Threatening Arrhythmias in Heart Failure Patients With Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 May;51(5):1422-1439. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26982. Epub 2019 Nov 11. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31710415
Cited by
-
The Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Parameters in Heart Failure.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 May 2;60(5):760. doi: 10.3390/medicina60050760. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38792942 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress and Heart Failure: Mechanisms, Signalling Pathways, and Therapeutics.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 14;2022:9829505. doi: 10.1155/2022/9829505. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35464761 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
miR-129-5p restores cardiac function in rats with chronic heart failure by targeting the E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 and promoting PTEN expression.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):2371-2386. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2024335. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35034538 Free PMC article.
-
Empagliflozin Ameliorates the Oxidative Stress Profile in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction: Results of a Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2025;20(2):167-179. doi: 10.2174/0115748871323540241212060946. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2025. PMID: 39779555 Clinical Trial.
-
The Impact of Pharmacotherapy for Heart Failure on Oxidative Stress-Role of New Drugs, Flozins.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 9;11(8):2236. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082236. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626732 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

