Maleate salts of bedaquiline
- PMID: 33936772
- PMCID: PMC8025853
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021002991
Maleate salts of bedaquiline
Abstract
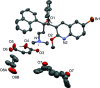
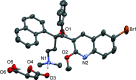
Bedaquiline is one of two important new drugs for the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB). It is marketed in the US as its fumarate salt, but only a few salts of bedaquiline have been structurally described so far. We present here five crystal structures of bedaquilinium maleate {systematic name: [4-(6-bromo-2-meth-oxy-quinolin-3-yl)-3-hy-droxy-3-(naphthalen-1-yl)-4-phenyl-but-yl]di-methyl-aza-nium 3-carb-oxy-prop-2-enoate}, C32H32BrN2O2 +·C4H3O4 -, namely, a hemihydrate, a tetra-hydro-furan (THF) solvate, a mixed acetone/hexane solvate, an ethyl acetate solvate, and a solvate-free structure obtained from the acetone/hexane solvate by in situ single-crystal-to-single-crystal desolvation. All salts exhibit a 1:1 cation-to-anion ratio, with the anion present as monoanionic hydro-maleate and a singly protonated bedaquilinium cation. The maleate exhibits the strong intra-molecular hydrogen bond typical for cis-di-carb-oxy-lic acid anions. The conformations of the cations and packing inter-actions in the maleate salts are compared to those of free base bedaquiline and other bedaquilinium salts.
Keywords: bedaquiline; crystal structure; desolvation; drug-resistant tuberculosis; isomorphous organic salts.
© Zeller et al. 2021.
Figures



 + x, −
+ x, − + y, z; (ii)
+ y, z; (ii)  + x,
+ x,  + y, z; (iii)
+ y, z; (iii)  + x,
+ x,  + y, z.
+ y, z.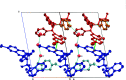
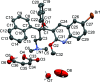
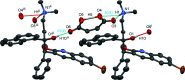
 10]). Hydrogen bonds are shown as turquoise dashed lines. Green dashed lines connect the centroids of the bromoquinoline substituents [3.432 (14) Å]. Partially occupied water molecules shown as spheres of arbitrary radius. For all other atoms, probability ellipsoids are at the 50% level. C-bound H atoms and labels for C H atoms are omitted for clarity.
10]). Hydrogen bonds are shown as turquoise dashed lines. Green dashed lines connect the centroids of the bromoquinoline substituents [3.432 (14) Å]. Partially occupied water molecules shown as spheres of arbitrary radius. For all other atoms, probability ellipsoids are at the 50% level. C-bound H atoms and labels for C H atoms are omitted for clarity.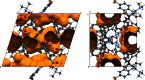

References
-
- Bruker (2020). APEX3 and SAINT. Bruker Nano Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. - PubMed
-
- European Chemical Agency (2015). Maleic Acid (CAS 110-16-7). Registered Substances Dossier. European Chemical Agency. Available from http://echa.europa.eu/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
