Isolated Basilic Vein Thrombosis as a Rare Presentation of COVID-19 in a Young Patient
- PMID: 33936889
- PMCID: PMC8081373
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14178
Isolated Basilic Vein Thrombosis as a Rare Presentation of COVID-19 in a Young Patient
Abstract
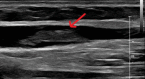
COVID-19 has not spared a single system in the human body. Although acute respiratory failure culminating sometimes in death remains the most common manifestation of severe infection, hypercoagulability leading to deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and stroke have also been identified widely. Here, we describe a young patient with a COVID-19 infection who developed right basilic vein thrombosis. This case demonstrates how thrombosis can occur in uncommon sites and how clinicians should be vigilant for thrombotic complications in both the inpatient and outpatient settings.
Keywords: anticoagulant prophylaxis; covid-19 pandemic; deep vein thrombosis (dvt); hypercoagulopathy; thromboinflammation; thromboprophylaxis; upper arm dvt.
Copyright © 2021, Acharya et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources