Clearing the Fog: Is Hydroxychloroquine Effective in Reducing Coronavirus Disease-2019 Progression? A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 33936897
- PMCID: PMC8083993
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14186
Clearing the Fog: Is Hydroxychloroquine Effective in Reducing Coronavirus Disease-2019 Progression? A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
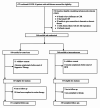
Background Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) has been considered for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), but data on its efficacy are conflicting. We analyzed the efficacy of HCQ along with standard of care (SOC) treatment, compared with SOC alone, in reducing disease progression in mild COVID-19. Methods A single-center open-label randomized controlled trial was conducted from April 10 to May 31, 2020 at Pak Emirates Military Hospital, Rawalpindi. Five hundred patients of both genders between the ages of 18 and 80 years with mild COVID-19 were enrolled in the study. A total of 349 patients were assigned to the intervention group (standard dose of HCQ plus SOC) and 151 patients were assigned to SOC only. The primary outcome was progression of disease while secondary outcome was polymerase chain reaction (PCR) negativity on days 7 and 14. The results were analyzed on Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY) version 23. A p-value <0.05 was considered significant. Results The median age of the intervention group was 34 ± 11.778 years and control group was 34 ± 9.813 years. Disease progressed in 16 patients, 11 (3.15%) of which were in the intervention group and 5 (3.3%) in the control group (p-value = 0.940). PCR negative cases in intervention and control groups on day 7 were 182 (52.1%) and 54 (35.8%), respectively (p-value = 0.001); and on day 14 were 244 (69.9%) and 110 (72.9%), respectively (p-value = 0.508). Consecutive PCR negativity on days 7 and 14 was observed in 240 (68.8%) patients in the intervention group compared to 106 (70.2%) in the control group (p-value = 0.321). Conclusion The addition of HCQ to SOC in hospitalized mild COVID-19 patients neither stops disease progression nor helps in early and sustained viral clearance.
Keywords: covid-19; disease progression; hcq; mild infection; rct; viral clearance.
Copyright © 2021, Kamran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Off-label Use of Medicines for COVID-19. [Jul;2020 ];https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/off-label-use-of-medic... 2020
-
- Infection Prevention and Control During Health Care When Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Is Suspected or Confirmed. [Jul;2020 ];https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-IPC-2020.4 2020
-
- Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. JAMA. 2020;323:1239–1242. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous