India's COVID-19 Burdens, 2020
- PMID: 33937163
- PMCID: PMC8079724
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.608810
India's COVID-19 Burdens, 2020
Abstract
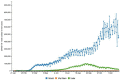
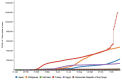
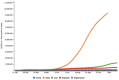
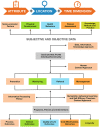
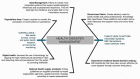
The purpose of this article is two pronged; first, to identify and report public health implications of the ongoing coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, and second, to report challenges uniquely faced by the citizens of India from a population health perspective. We have done both while closely examining epidemiological data that is accessible via SMAART's RAPID Tracker. This policy informatics platform is a live database aimed to track the geospatial spread of the COVID-19 outbreak and policy actions globally and is administered collaboratively by CUNY's Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy and a global, non-profit public health incubator. Infectivity, incidence, and recovery rates were computed and graphical representations of epidemiological datasets were studied. We have discussed a plausible conceptual framework based on the principles of population health informatics for countries with similar characteristics to build a stronger public and community health foundation in order to safeguard populations during a health emergency in the future.
Keywords: COVID-19; India; SMAART RAPID tracker; public health; public policy.
Copyright © 2021 Joshi, Mewani, Arora and Grover.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
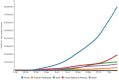
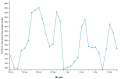
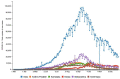
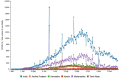
References
-
- Dashboard - World . SMAART RapidTracker: A Global Policy Informatics Tool to Track COVID-19 Outbreak (Corona Virus Disease Outbreak). (2020). Available online at: http://www.smaartrapidtracker.org/dashboard-world/ (accessed August 21, 2020).
-
- Gates B. How the Pandemic Will Shape the Near Future. Ted.com. (2020). Available online at: https://www.ted.com/talks/bill_gates_how_the_pandemic_will_shape_the_nea... (accessed September 12, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

