Experimental and natural evidence of SARS-CoV-2-infection-induced activation of type I interferon responses
- PMID: 33937724
- PMCID: PMC8074517
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102477
Experimental and natural evidence of SARS-CoV-2-infection-induced activation of type I interferon responses
Abstract
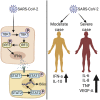
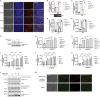
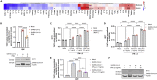
Type I interferons (IFNs) are our first line of defense against virus infection. Recent studies have suggested the ability of SARS-CoV-2 proteins to inhibit IFN responses. Emerging data also suggest that timing and extent of IFN production is associated with manifestation of COVID-19 severity. In spite of progress in understanding how SARS-CoV-2 activates antiviral responses, mechanistic studies into wild-type SARS-CoV-2-mediated induction and inhibition of human type I IFN responses are scarce. Here we demonstrate that SARS-CoV-2 infection induces a type I IFN response in vitro and in moderate cases of COVID-19. In vitro stimulation of type I IFN expression and signaling in human airway epithelial cells is associated with activation of canonical transcriptions factors, and SARS-CoV-2 is unable to inhibit exogenous induction of these responses. Furthermore, we show that physiological levels of IFNα detected in patients with moderate COVID-19 is sufficient to suppress SARS-CoV-2 replication in human airway cells.
Keywords: Immunology; Virology.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Arabi Y.M., Asiri A.Y., Assiri A.M., Aziz Jokhdar H.A., Alothman A., Balkhy H.H., AlJohani S., Al Harbi S., Kojan S., Al Jeraisy M. Treatment of Middle East respiratory syndrome with a combination of lopinavir/ritonavir and interferon-beta1b (MIRACLE trial): statistical analysis plan for a recursive two-stage group sequential randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2020;21:8. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

