Pathogenesis of Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti in TLR4-Competent and TLR4-dysfunctional C3H mice
- PMID: 33938125
- PMCID: PMC8459286
- DOI: 10.1111/cmi.13350
Pathogenesis of Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti in TLR4-Competent and TLR4-dysfunctional C3H mice
Abstract
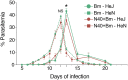
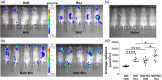
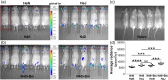
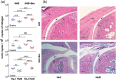
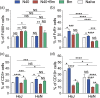
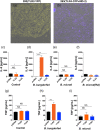
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of membrane-spanning proteins of host cells. TLR2 and TLR4 are displayed on the surface of macrophages, neutrophils and dendritic cells and recognise structurally conserved microbial signatures defined as Pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). C3H mice are susceptible to tick-borne pathogens; Lyme disease causing Borrelia burgdorferi that manifests arthritis and carditis and Apicomplexan protozoan, Babesia microti (Bm) that causes significant parasitemia associated with erythrocytopenia and haemoglobinuria. B. burgdorferi lacks typical TLR4 ligand lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and Bm TLR ligand(s) remain unknown. Only Borrelia lipoproteins that signal through TLR2 are established as PAMPs of these pathogens for TLR2/TLR4. Infection of C3H mice with each pathogen individually resulted in increase in the percentage of splenic B, T and FcR+ cells while their co-infection significantly diminished levels of these cells and caused increased B. burgdorferi burden in the specific organs. The most pronounced inflammatory arthritis was observed in co-infected C3H/HeJ mice. Parasitemia levels and kinetics of resolution of Bm in both mice strains were not significantly different. Transfected HEK293 cells showed pronounced signalling by B. burgdorferi through TLR2 and to some extent by TLR4 while Bm and infected erythrocytes did not show any response confirming our results in mice.
Keywords: Babesia microti; Babesiosis; Borrelia burgdorferi; Lyme disease; co-infection; inflammation; toll like receptor 4.
© 2021 The Authors. Cellular Microbiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdollahi‐Roodsaz, S., Koenders, M. I., Walgreen, B., Bolscher, J., Helsen, M. M., van den Bersselaar, L. A., … van den Berg, W. B. (2013). Toll‐like receptor 2 controls acute immune complex‐driven arthritis in mice by regulating the inhibitory Fcgamma receptor IIB. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 65(10), 2583–2593. 10.1002/art.38087 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aliota, M. T., Dupuis, A. P., 2nd, Wilczek, M. P., Peters, R. J., Ostfeld, R. S., & Kramer, L. D. (2014). The prevalence of zoonotic tick‐borne pathogens in Ixodes scapularis collected in the Hudson Valley, New York state. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 14(4), 245–250. 10.1089/vbz.2013.1475 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, A. L., Barthold, S. W., Persing, D. H., & Beck, D. S. (1992). Carditis in Lyme disease susceptible and resistant strains of laboratory mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi . The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 47(2), 249–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

