Spontaneous pulmonary artery thrombus in a neonate
- PMID: 33939053
- PMCID: PMC8091146
- DOI: 10.1186/s43044-021-00167-4
Spontaneous pulmonary artery thrombus in a neonate
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Spontaneous pulmonary artery thrombus in a neonate.Egypt Heart J. 2021 May 13;73(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s43044-021-00169-2. Egypt Heart J. 2021. PMID: 33987700 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
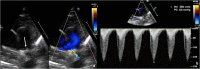
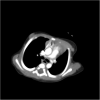
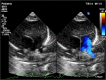
Background: Pulmonary artery thrombosis is rare in neonates and mimics as persistent pulmonary hypertension or congenital heart disease. Risk factors include septicemia, dehydration, polycythemia, maternal diabetes, asphyxia, and inherited thrombophilias. They present with cyanosis and respiratory distress. Careful echocardiogram assessment helps in identifying the thrombus in the pulmonary artery and its branches. Computed tomography pulmonary angiography confirms the diagnosis.
Case presentation: We present a case of term neonate who presented with respiratory distress and cyanosis and a detailed echocardiogram revealed thrombus in the origin of left pulmonary artery. The neonate was managed initially with unfractionated heparin and later with low molecular weight heparin with which there was significant resolution of the thrombus CONCLUSION: Spontaneous pulmonary artery thrombosis though rare should be suspected in any cyanotic neonate with respiratory distress. Management in these cases depends on the haemodynamic instability and lung ischemia.
Keywords: Computed tomography pulmonary angiography; Echocardiogram; Persistent pulmonary artery hypertension; Pulmonary artery thrombus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
