Low rate of relapse after twelve-dose multidrug therapy for hansen's disease: A 20-year cohort study in a brazilian reference center
- PMID: 33939710
- PMCID: PMC8118692
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009382
Low rate of relapse after twelve-dose multidrug therapy for hansen's disease: A 20-year cohort study in a brazilian reference center
Abstract
The World Health Organization has raised concerns about the increasing number of Hansen disease (HD) relapses worldwide, especially in Brazil, India, and Indonesia that report the highest number of recurrent cases. Relapses are an indicator of MDT effectiveness and can reflect Mycobacterium leprae persistence or re-infection. Relapse is also a potential marker for the development or progression of disability. In this research, we studied a large cohort of persons affected by HD treated with full fixed-dose multibacillary (MB) multidrug therapy (MDT) followed for up to 20 years and observed that relapses are a rare event. We estimated the incidence density of relapse in a cohort of patients classified to receive MB regime (bacillary index (BI) > 0), diagnosed between September 1997 and June 2017, and treated with twelve-dose MB-MDT at a HD reference center in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. We obtained the data from the data management system of the clinic routine service. We linked the selected cases to the dataset of relapses of the national HD data to confirm possible relapse cases diagnosed elsewhere. We diagnosed ten cases of relapse in a cohort of 713 patients followed-up for a mean of 12.1 years. This resulted in an incidence rate of 1.16 relapse cases per 1000 person-year (95% CI = 0.5915-2.076). The accumulated risk was 0.025 in 20 years. The very low risk observed in this cohort of twelve-dose-treated MB patients reinforces the success of the current MDT scheme.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
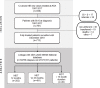
Figures


Similar articles
-
OFLOXACIN multicentre trial in MB leprosy FUAM-Manaus and ILSL-Bauru, Brazil.Lepr Rev. 2012 Sep;83(3):261-8. Lepr Rev. 2012. PMID: 23356027 Clinical Trial.
-
Daily multidrug therapy for leprosy; results of a fourteen-year experience.Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1997 Mar;65(1):37-44. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1997. PMID: 9207752 Clinical Trial.
-
Late relapses in leprosy patients in Brazil: 10-year post-trial of uniform multidrug therapy (U-MDT/CT-BR).Braz J Infect Dis. 2024 Mar-Apr;28(2):103745. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2024.103745. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Braz J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38697216 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Relapses among leprosy patients treated with multidrug therapy: experience in the leprosy control program of the All Africa Leprosy and Rehabilitation Training Center (ALERT) in Ethiopia; practical difficulties with diagnosing relapses; operational procedures and criteria for diagnosing relapses.Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1992 Sep;60(3):421-35. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1992. PMID: 1474281 Review.
-
Leprosy - an overview of clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment.J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2017 Aug;15(8):801-827. doi: 10.1111/ddg.13301. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2017. PMID: 28763601 Review.
Cited by
-
Mycobacterium leprae's Infective Capacity Is Associated with Activation of Genes Involved in PGL-I Biosynthesis in a Schwann Cells Infection Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 13;24(10):8727. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108727. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240073 Free PMC article.
-
Role of histopathological, serological and molecular findings for the early diagnosis of treatment failure in leprosy.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 1;24(1):1085. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09937-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39354399 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression patterns associated with multidrug therapy in multibacillary leprosy.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 22;12:917282. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.917282. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35937686 Free PMC article.
-
Autochthonous North American Leprosy: A Second Case in Canada.Infect Dis Rep. 2021 Oct 22;13(4):917-923. doi: 10.3390/idr13040083. Infect Dis Rep. 2021. PMID: 34698226 Free PMC article.
-
Leprosy.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024 Nov 28;10(1):90. doi: 10.1038/s41572-024-00575-1. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024. PMID: 39609422 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Twenty-five years of multidrug therapy for leprosy. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2004, 79:247–252. Available from: https://www.who.int/wer/2004/wer7927/en/. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global leprosy update, 2018: need for early case detection. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2019;94, 389–412. Available from: https://www.who.int/wer/2019/wer9435_36/en/.
-
- World Health Organization. Global leprosy (Hansen disease) update, 2019. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2020;95, 417–440. Available from: https://www.who.int/wer/2020/wer9536/en/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

