Acquired Resistance Mechanism of EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication to EGFR TKIs in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 33940786
- PMCID: PMC8756122
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2021.385
Acquired Resistance Mechanism of EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication to EGFR TKIs in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Epidermal growth factor receptor kinase domain duplication (EGFR-KDD) is a rare and poorly understood oncogenic mutation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We aimed to investigate the acquired resistance mechanism of EGFR-KDD against EGFR-TKIs.
Materials and methods: We identified EGFR-KDD in tumor tissue obtained from a patient with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma and established the patient-derived cell line SNU-4784. We also established several EGFR-KDD Ba/F3 cell lines: EGFR-KDD wild type (EGFR-KDDWT), EGFR-KDD domain 1 T790M (EGFR-KDDD1T), EGFR-KDD domain 2 T790M (EGFR-KDDD2T), and EGFR-KDD both domain T790M (EGFR-KDDBDT). We treated the cells with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and performed cell viability assays, immunoblot assays, and ENU (N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea) mutagenesis screening.
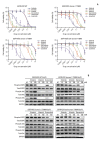
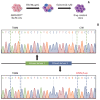
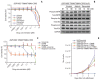
Results: In cell viability assays, SNU-4784 cells and EGFR-KDDWT Ba/F3 cells were sensitive to 2nd generation and 3rd generation EGFR TKIs. In contrast, the T790M-positive EGFR-KDD Ba/F3 cell lines (EGFR-KDDT790M) were only sensitive to 3rd generation EGFR TKIs. In ENU mutagenesis screening, we identified the C797S mutation in kinase domain 2 of EGFR-KDDBDT Ba/F3 cells. Based on this finding, we established an EGFR-KDD domain 1 T790M/domain 2 cis-T790M+C797S (EGFR-KDDT/T+C) Ba/F3 model, which was resistant to EGFR TKIs and anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody combined with EGFR TKIs.
Conclusion: Our study reveals that the T790M mutation in EGFR-KDD confers resistance to 1st and 2nd generation EGFR TKIs, but is sensitive to 3rd generation EGFR TKIs. In addition, we identified that the C797S mutation in kinase domain 2 of EGFR-KDDT790M mediates a resistance mechanism against 3rd generation EGFR TKIs.
Keywords: Acquired resistance; EGFR C797S mutation; EGFR T790M mutation; EGFR kinase domain duplication; Non–small cell lung carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. D-W Kim’s Institution (Seoul National University Hospital) received grants from Alpha Biopharma, Amgen, Astrazeneca/Medimmune, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, Hanmi, Janssen, Merus, Mirati Therapeutics, MSD, Novartis, ONO Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Takeda, TP Therapeutics, Xcovery and Yuhan. In addition, Dr. D-W Kim received travel and accommodation support for advisory board meeting attendance from Amgen and Daiichi-Sankyo. All these COI’s are outside of the submitted work. The other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line PC-9 Drug-resistant Mutant Cell Line Establishment and Validation of Their Sensitivity to EGFR Inhibitors].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024 Nov 20;27(11):815-825. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2024.101.31. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39800476 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Audit of Molecular Mechanisms of Primary and Secondary Resistance to Various Generations of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Known Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients in a Tertiary Centre.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022 Nov;34(11):e451-e462. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022. PMID: 35810049
-
EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancers Resistant to Osimertinib through EGFR C797S Respond to First-Generation Reversible EGFR Inhibitors but Eventually Acquire EGFR T790M/C797S in Preclinical Models and Clinical Samples.J Thorac Oncol. 2019 Nov;14(11):1995-2002. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.07.016. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Thorac Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31377341 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting EGFRL858R/T790M and EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S resistance mutations in NSCLC: Current developments in medicinal chemistry.Med Res Rev. 2018 Sep;38(5):1550-1581. doi: 10.1002/med.21488. Epub 2018 Jan 26. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29377179 Review.
-
Transformation from acquired EGFR 19del/C797S to EGFR 19del/T790M in an advanced non-small cell lung cancer patient: a case report and literature review.Anticancer Drugs. 2025 Jul 1;36(6):513-517. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001707. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Anticancer Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39960762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Colorectal cancer harboring EGFR kinase domain duplication response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Oncologist. 2025 Feb 6;30(2):oyae113. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyae113. Oncologist. 2025. PMID: 38821532 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Screening and Biological Evaluation of T22306 as a Potent Third-generation EGFR Inhibitor for NSCLC Treatment.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025;25(15):1128-1141. doi: 10.2174/0118715206362954250203103859. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39931859
-
A Constitutive EGFR Kinase Dimer to Study Inhibitor Pharmacology.Mol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;105(2):97-103. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.123.000768. Mol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38164587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553:446–54. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

