An ionising radiation-induced specific transcriptional signature of inflammation-associated genes in whole blood from radiotherapy patients: a pilot study
- PMID: 33941218
- PMCID: PMC8094544
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-021-01807-4
An ionising radiation-induced specific transcriptional signature of inflammation-associated genes in whole blood from radiotherapy patients: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: This communication reports the identification of a new panel of transcriptional changes in inflammation-associated genes observed in response to ionising radiation received by radiotherapy patients.
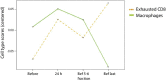
Methods: Peripheral blood samples were taken with ethical approval and informed consent from a total of 20 patients undergoing external beam radiotherapy for breast, lung, gastrointestinal or genitourinary tumours. Nanostring nCounter analysis of transcriptional changes was carried out in samples prior and 24 h post-delivery of the 1st radiotherapy fraction, just prior to the 5th or 6th fraction, and just before the last fraction.
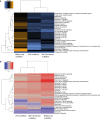
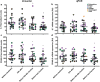
Results: Statistical analysis with BRB-ArrayTools, GLM MANOVA and nSolver, revealed a radiation responsive panel of genes which varied by patient group (type of cancer) and with time since exposure (as an analogue for dose received), which may be useful as a biomarker of radiation response.
Conclusion: Further validation in a wider group of patients is ongoing, together with work towards a full understanding of patient specific responses in support of personalised approaches to radiation medicine.
Keywords: Blood; Cancer; Gene expression; Inflammation; Ionising radiation; NCounter; RT-qPCR; Radiotherapy; Transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Abend M, Badie C, Quintens R, Kriehuber R, Manning G, Macaeva E, et al. Examining radiation-induced in vivo and in vitro gene expression changes of the peripheral blood in different laboratories for biodosimetry purposes: first RENEB gene expression study. Radiat Res. 2016;185(2):109–123. doi: 10.1667/RR14221.1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ainsbury E, Badie C, Barnard S, Manning G, Moquet J, Abend M, et al. Integration of new biological and physical retrospective dosimetry methods into EU emergency response plans—joint RENEB and EURADOS inter-laboratory comparisons. Int J Radiat Biol. 2017;93(1):99–109. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2016.1206233. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

