Inhibition of Jumonji Histone Demethylases Selectively Suppresses HER2+ Breast Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Growth via Inhibition of GMCSF Expression
- PMID: 33941612
- PMCID: PMC9126130
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3317
Inhibition of Jumonji Histone Demethylases Selectively Suppresses HER2+ Breast Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Growth via Inhibition of GMCSF Expression
Abstract
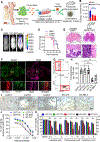
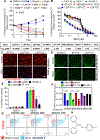
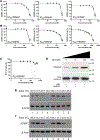
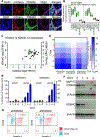
HER2+ breast leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (HER2+ LC) occurs when tumor cells spread to cerebrospinal fluid-containing leptomeninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord, a complication with a dire prognosis. HER2+ LC remains incurable, with few treatment options. Currently, much effort is devoted toward development of therapies that target mutations. However, targeting epigenetic or transcriptional states of HER2+ LC tumors might efficiently target HER2+ LC growth via inhibition of oncogenic signaling; this approach remains promising but is less explored. To test this possibility, we established primary HER2+ LC (Lepto) cell lines from nodular HER2+ LC tissues. These lines are phenotypically CD326+CD49f-, confirming that they are derived from HER2+ LC tumors, and express surface CD44+CD24-, a cancer stem cell (CSC) phenotype. Like CSCs, Lepto lines showed greater drug resistance and more aggressive behavior compared with other HER2+ breast cancer lines in vitro and in vivo. Interestingly, the three Lepto lines overexpressed Jumonji domain-containing histone lysine demethylases KDM4A/4C. Treatment with JIB04, a selective inhibitor of Jumonji demethylases, or genetic loss of function of KDM4A/4C induced apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest and reduced Lepto cell viability, tumorsphere formation, regrowth, and invasion in vitro. JIB04 treatment of patient-derived xenograft mouse models in vivo reduced HER2+ LC tumor growth and prolonged animal survival. Mechanistically, KDM4A/4C inhibition downregulated GMCSF expression and prevented GMCSF-dependent Lepto cell proliferation. Collectively, these results establish KDM4A/4C as a viable therapeutic target in HER2+ LC and spotlight the benefits of targeting the tumorigenic transcriptional network. SIGNIFICANCE: HER2+ LC tumors overexpress KDM4A/4C and are sensitive to the Jumonji demethylase inhibitor JIB04, which reduces the viability of primary HER2+ LC cells and increases survival in mouse models.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


References
-
- Brown DA, Lu VM, Himes BT, Burns TC, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Chaichana KL, et al. Breast brain metastases are associated with increased risk of leptomeningeal disease after stereotactic radiosurgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Metastasis 2020;37:341–52 - PubMed
-
- DeAngelis LM. Current diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal metastasis. J Neurooncol 1998;38:245–52 - PubMed
-
- DeAngelis LM, Boutros D. Leptomeningeal metastasis. Cancer Invest 2005;23:145–54 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

