A Role for VCP/p97 in the Processing of Drug-Stabilized TOP2-DNA Covalent Complexes
- PMID: 33941661
- PMCID: PMC7611185
- DOI: 10.1124/molpharm.121.000262
A Role for VCP/p97 in the Processing of Drug-Stabilized TOP2-DNA Covalent Complexes
Abstract
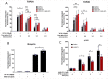
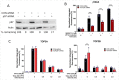
DNA topoisomerase II (TOP2) poisons induce protein-DNA crosslinks termed TOP2-DNA covalent complexes, in which TOP2 remains covalently bound to each end of an enzyme-induced double-strand DNA break (DSB) via a 5'-phosphotyrosyl bond. Repair of the enzyme-induced DSB first requires the removal of the TOP2 protein adduct, which, among other mechanisms, can be accomplished through the proteasomal degradation of TOP2. VCP/p97 is a AAA ATPase that utilizes energy from ATP hydrolysis to unfold protein substrates, which can facilitate proteasomal degradation by extracting target proteins from certain cellular structures (such as chromatin) and/or by aiding their translocation into the proteolytic core of the proteasome. In this study, we show that inhibition of VCP/p97 leads to the prolonged accumulation of etoposide-induced TOP2A and TOP2B complexes in a manner that is epistatic with the proteasomal pathway. VCP/p97 inhibition also reduces the etoposide-induced phosphorylation of histone H2A.X, indicative of fewer DSBs. This suggests that VCP/p97 is required for the proteasomal degradation of TOP2-DNA covalent complexes and is thus likely to be an important mediator of DSB repair after treatment with a TOP2 poison. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: TOP2 poisons are chemotherapeutic agents used in the treatment of a range of cancers. A better understanding of how TOP2 poison-induced DNA damage is repaired could improve therapy with TOP2 poisons by increasing TOP2 poison cytotoxicity and reducing genotoxicity. The results presented herein suggest that repair of TOP2-DNA covalent complexes involves the protein segregase VCP/p97.
Copyright © 2021 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Acs K, Luijsterburg MS, Ackermann L, Salomons FA, Hoppe T, Dantuma NP. The AAA-ATPase VCP/p97 promotes 53BP1 recruitment by removing L3MBTL1 from DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18(12):1345–1350. - PubMed
-
- Alchanati I, Teicher C, Cohen G, Shemesh V, Barr HM, Nakache P, Ben-Avraham D, Idelevich A, Angel I, Livnah N, Tuvia S, et al. The E3 ubiquitin-ligase Bmi1/Ring1A controls the proteasomal degradation of Top2alpha cleavage complex-a potentially new drug target. PLoS One. 2009;4(12):e8104. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beskow A, Grimberg KB, Bott LC, Salomons FA, Dantuma NP, Young P. A Conserved Unfoldase Activity for the p97 AAA-ATPase in Proteasomal Degradation. Journal of Molecular Biology. 2009;394(4):732–746. - PubMed
-
- Bromberg KD, Burgin AB, Osheroff N. A two-drug model for etoposide action against human topoisomerase IIalpha. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(9):7406–7412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

