Assessment of municipal solid waste management system in Lae City, Papua New Guinea in the context of sustainable development
- PMID: 33942012
- PMCID: PMC8081651
- DOI: 10.1007/s10668-021-01465-2
Assessment of municipal solid waste management system in Lae City, Papua New Guinea in the context of sustainable development
Abstract
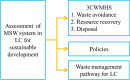
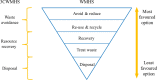
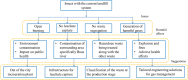
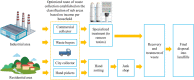
Abstract: Lae City (LC) of Morobe Province is the second-largest city in Papua New Guinea. Due to the abundant natural resources it inherits, the resultant urbanization has led to an influx of the human population. This increase in population as a result of industrialization has led to increased municipal solid waste (MSW) accumulation. To address this exigent issue, which affects the nation's carbon footprint, it is imperative to review socio-economic and geographic factors to establish a feasible approach for managing MSW efficiently and sustainably. In the quest to achieve the same, the present assessment focuses on the 3 core waste management hierarchy systems to support sustainable development for LC by reviewing existing opportunities and challenges associated with the current MSW management system and the associated policies. The result shows that as a sustainable approach to MSW management of LC, a zero-waste campaign for resource recovery engaging all stakeholders can be implemented since the organic content of MSW generated in LC is as high as 70%. Moreover, the dumping of MSW at the dedicated dumpsite site can be minimized if policies are strengthened and the proposed waste avoidance pathway is implemented strictly. In addition to this, to avoid the contamination of groundwater and recovery of methane, the use of the Fukuoka approach in the existing landfills has been suggested to capture leachate without any huge expenditure.
Keywords: Fukuoka method; Landfill; Municipal solid waste; Resource recovery; Waste avoidance; Waste management hierarchy 3 core systems.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestThe authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Abad, V., Avila, R., Vicent, T., & Font, X. (2019). Promoting circular economy in the surroundings of an organic fraction of municipal solid waste anaerobic digestion treatment plant: Biogas production impact and economic factors. Bioresource Technology, 283, 10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.064 - PubMed
-
- Abd El-Salam, M. M., & I. Abu-Zuid, G. (2015). Impact of landfill leachate on the groundwater quality: A case study in Egypt. Journal of Advanced Research, 6(4), 579–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2014.02.003 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adam, M. G., Tran, P. T. M., Bolan, N., & Balasubramanian, R. (2021). Biomass burning-derived airborne particulate matter in Southeast Asia: A critical review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 407, 124760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124760 - PubMed
-
- Adelodun, B., Kim, S. H., & Choi, K.-S. (2021). Assessment of food waste generation and composition among Korean households using novel sampling and statistical approaches. Waste Management, 122, 71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.01.003 - PubMed
-
- Agapios, A., Andreas, V., Marinos, S., Katerina, M., & Antonis, Z. A. (2020). Waste aroma profile in the framework of food waste management through household composting. Journal of Cleaner Production, 257, 120340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120340
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
