Individual-Specific Areal-Level Parcellations Improve Functional Connectivity Prediction of Behavior
- PMID: 33942058
- PMCID: PMC8757323
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhab101
Individual-Specific Areal-Level Parcellations Improve Functional Connectivity Prediction of Behavior
Abstract
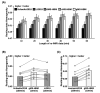
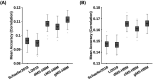
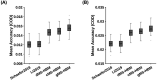
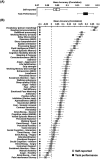
Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) allows estimation of individual-specific cortical parcellations. We have previously developed a multi-session hierarchical Bayesian model (MS-HBM) for estimating high-quality individual-specific network-level parcellations. Here, we extend the model to estimate individual-specific areal-level parcellations. While network-level parcellations comprise spatially distributed networks spanning the cortex, the consensus is that areal-level parcels should be spatially localized, that is, should not span multiple lobes. There is disagreement about whether areal-level parcels should be strictly contiguous or comprise multiple noncontiguous components; therefore, we considered three areal-level MS-HBM variants spanning these range of possibilities. Individual-specific MS-HBM parcellations estimated using 10 min of data generalized better than other approaches using 150 min of data to out-of-sample rs-fMRI and task-fMRI from the same individuals. Resting-state functional connectivity derived from MS-HBM parcellations also achieved the best behavioral prediction performance. Among the three MS-HBM variants, the strictly contiguous MS-HBM exhibited the best resting-state homogeneity and most uniform within-parcel task activation. In terms of behavioral prediction, the gradient-infused MS-HBM was numerically the best, but differences among MS-HBM variants were not statistically significant. Overall, these results suggest that areal-level MS-HBMs can capture behaviorally meaningful individual-specific parcellation features beyond group-level parcellations. Multi-resolution trained models and parcellations are publicly available (https://github.com/ThomasYeoLab/CBIG/tree/master/stable_projects/brain_parcellation/Kong2022_ArealMSHBM).
Keywords: behavioral prediction; brain parcellation; difference; individual; resting-state functional connectivity.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



References
-
- Amunts K, Zilles K. 2015. Architectonic mapping of the human brain beyond Brodmann. Neuron. 88:1086–1107. - PubMed
-
- Arslan S, Parisot S, Rueckert D. 2015. Joint spectral decomposition for the parcellation of the human cerebral cortex using resting-state fMRI. In: Ourselin S, Alexander DC, Westin C-F, Cardoso MJ, editors. Information processing in medical imaging. Springer International Publishing: Cham, pp. 85–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

