Preliminary testing and evaluation of the renata minima stent, an infant stent capable of achieving adult dimensions
- PMID: 33942962
- PMCID: PMC9543198
- DOI: 10.1002/ccd.29706
Preliminary testing and evaluation of the renata minima stent, an infant stent capable of achieving adult dimensions
Abstract
Objectives: This study sought to obtain in vivo data on a new stent and delivery system specifically designed for implantation in infants with the ability to be enlarged to adult dimensions.
Background: There are no endovascular stents designed for or approved for use in infants, nor is there a stent capable of being implanted at infant vessel diameters and achieving adult size while maintaining structural integrity. The Minima stent was designed to address these needs.
Methods: This study was performed in 6 piglets who underwent implantation of 22 Minima stents into the following locations: aorta (n = 11), branch pulmonary arteries (n = 6), and central veins (n = 5).
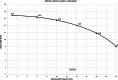
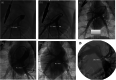
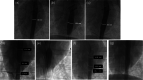
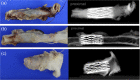
Results: Successful deployment occurred in 21/22 attempts. Two instances of post-deployment migration occurred. Stents were re-expanded at 1, 2, 3 and 5 months after implant. All stents regardless of location could be re-dilated to the intended diameter to keep pace with somatic growth (implant diameter 6.9 +/- 1.2 mm; final diameter 16.1 mm +/- 1.4 mm). Histopathology at 1 and 5 months demonstrated widely patent vessel lumens with stent apposition to vessel wall, early mild inflammatory response surrounding stent struts, typical vascular damage and healing response to acute dilation and a progressive smooth neointimal growth covering stent struts over time.
Conclusions: In this in vivo study of the Minima stent, there was high implant success, predictable re-dilatability to adult diameters and favorable histopathology. Further study is warranted.
Keywords: congenital heart disease; pediatric intervention; stent; vascular stenosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Evan M. Zahn is Medical Director, Renata Medical. Mr. Eason Abbott and Dustin Armer are officers of Renata Medical.
Figures





References
-
- Mullins CE, O'Laughlin MP, Vick GW 3rd, et al. Implantation of balloon‐expandable intravascular grafts by catheterization in pulmonary arteries and systemic veins. Circulation. 1988;77:188‐199. - PubMed
-
- Stanfill R, Nykanen DG, Osorio S, Whalen R, Burke RP, Zahn EM. Stent implantation is effective treatment of vascular stenosis in young infants with congenital heart disease: acute implantation and long‐term follow‐up results. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008;71(6):831‐841. - PubMed
-
- Ooi YK, Kim SIH, Gillespie SE, Kim DW, Vincent RN, Petit CJ. Premounted stents for branch pulmonary artery stenosis in children: a short term solution. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;92(7):1315‐1322. - PubMed
-
- Abraham BP, Gilliam E, Kim DW, Wolf MJ, Vincent RN, Petit CJ. Early catheterization after initiation of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support in children is associated with improved survival. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;88(4):592‐599. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

