Polygenic risk score for genetic evaluation of prostate cancer risk in Asian populations: A narrative review
- PMID: 33943048
- PMCID: PMC8100017
- DOI: 10.4111/icu.20210124
Polygenic risk score for genetic evaluation of prostate cancer risk in Asian populations: A narrative review
Abstract
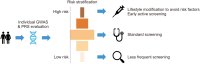
Decreasing costs of genetic testing and interest in disease inheritance has changed the landscape of cancer prediction in prostate cancer (PCa), and guidelines now include genetic testing for high-risk groups. Familial and hereditary PCa comprises approximately 20% and 5% of all PCa, respectively. Multifaceted disorders like PCa are caused by a combinatory effect of rare genes of high penetrance and smaller genetic variants of relatively lower effect size. Polygenic risk score (PRS) is a novel tool utilizing PCa-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) identified from genome-wide association study (GWAS) to generate an additive estimate of an individual's lifetime genetic risk for cancer. However, most PRS are developed based on GWAS collected from mainly European populations and do not address ethnic differences in PCa genetics. This review highlights the attempts to generate a PRS tailored to Asian males including data from Korea, China, and Japan, and discuss the clinical implications for prediction of early onset and aggressive PCa.
Keywords: Multifactorial inheritance; Polygenic traits; Prostatic neoplasms.
© The Korean Urological Association, 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Seok-Soo Byun is concurrently employed by PROCAGEN.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prostate cancer risk-associated genetic markers and their potential clinical utility.Asian J Androl. 2013 May;15(3):314-22. doi: 10.1038/aja.2013.42. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Asian J Androl. 2013. PMID: 23564047 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of reported prostate cancer risk-associated SNPs from genome-wide association studies of various racial populations in Chinese men.Prostate. 2013 Nov;73(15):1623-35. doi: 10.1002/pros.22629. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Prostate. 2013. PMID: 24038036 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive performance of prostate cancer risk in Chinese men using 33 reported prostate cancer risk-associated SNPs.Prostate. 2012 Apr;72(5):577-83. doi: 10.1002/pros.21462. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Prostate. 2012. PMID: 21796652 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic risk score in prostate cancer.Curr Opin Urol. 2022 Sep 1;32(5):466-471. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0000000000001029. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Curr Opin Urol. 2022. PMID: 35855560 Review.
-
Polygenic Risk Scores in Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment and Screening.Urol Clin North Am. 2021 Aug;48(3):387-399. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2021.03.007. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Urol Clin North Am. 2021. PMID: 34210493 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive value of polygenic risk score for prostate cancer incidence and prognosis in the Han Chinese.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 3;14(1):20453. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71544-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39227454 Free PMC article.
-
The Combined Effect of Polygenic Risk Score and Prostate Health Index in Chinese Men Undergoing Prostate Biopsy.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 8;12(4):1343. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041343. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36835879 Free PMC article.
-
Race and prostate cancer: genomic landscape.Nat Rev Urol. 2022 Sep;19(9):547-561. doi: 10.1038/s41585-022-00622-0. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Nat Rev Urol. 2022. PMID: 35945369 Review.
-
Association of Androgen Deprivation Therapy with Osteoporotic Fracture in Patients with Prostate Cancer with Low Tumor Burden Using a Retrospective Population-Based Propensity-Score-Matched Cohort.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 18;15(10):2822. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102822. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345162 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic risk score for tumor aggressiveness and early-onset prostate cancer in Asians.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 16;13(1):798. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17515-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36646726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kimura T, Egawa S. Epidemiology of prostate cancer in Asian countries. Int J Urol. 2018;25:524–531. - PubMed
-
- de Bono J, Mateo J, Fizazi K, Saad F, Shore N, Sandhu S, et al. Olaparib for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:2091–2102. - PubMed
-
- Clarke N, Wiechno P, Alekseev B, Sala N, Jones R, Kocak I, et al. Olaparib combined with abiraterone in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:975–986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical