Optimal timing and criteria of interim PET in DLBCL: a comparative study of 1692 patients
- PMID: 33944897
- PMCID: PMC8114547
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004467
Optimal timing and criteria of interim PET in DLBCL: a comparative study of 1692 patients
Abstract
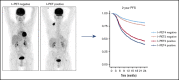
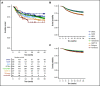
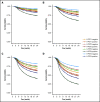
Interim 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (Interim-18F-FDG-PET, hereafter I-PET) has the potential to guide treatment of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) if the prognostic value is known. The aim of this study was to determine the optimal timing and response criteria for evaluating prognosis with I-PET in DLBCL. Individual patient data from 1692 patients with de novo DLBCL were combined and scans were harmonized. I-PET was performed at various time points during treatment with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) therapy. Scans were interpreted using the Deauville score (DS) and change in maximum standardized uptake value (ΔSUVmax). Multilevel Cox proportional hazards models corrected for International Prognostic Index (IPI) score were used to study the effects of timing and response criteria on 2-year progression-free survival (PFS). I-PET after 2 cycles (I-PET2) and I-PET4 significantly discriminated good responders from poor responders, with the highest hazard ratios (HRs) for I-PET4. Multivariable HRs for a PET-positive result at I-PET2 and I-PET4 were 1.71 and 2.95 using DS4-5, 4.91 and 6.20 using DS5, and 2.93 and 4.65 using ΔSUVmax, respectively. ΔSUVmax identified a larger proportion of poor responders than DS5 did. For all criteria, the negative predictive value was >80%, and positive predictive values ranged from 30% to 70% at I-PET2 and I-PET4. Unlike I-PET1, I-PET3 discriminated good responders from poor responders using DS4-5 and DS5 thresholds (HRs, 2.94 and 4.67, respectively). I-PET2 and I-PET4 predict good response equally during R-CHOP therapy in DLBCL. Optimal timing and response criteria depend on the clinical context. Good response at I-PET2 is suggested for de-escalation trials, and poor response using ΔSUVmax at I-PET4 is suggested for randomized trials that are evaluating new therapies.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: U.D. received research funding from Amgen and Roche and honoraria for participating in advisory boards from Amgen and Roche. P.J.L. received research funding from Takeda, Servier, and Roche and honoraria for participating in advisory boards from Takeda, Servier, Roche, Genmab, Celgene, Regeneron, and Incyte. S.F.B. is on the speakers bureau for Takeda and Hoffman la Roche and received departmental funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Amgen. J.M.Z. received research funding from Roche and received honoraria for participating in advisory boards from Takeda, Gilead, and Roche. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project . A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):987-994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

