The deacylase SIRT5 supports melanoma viability by influencing chromatin dynamics
- PMID: 33945506
- PMCID: PMC8203465
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI138926
The deacylase SIRT5 supports melanoma viability by influencing chromatin dynamics
Abstract
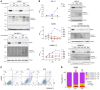
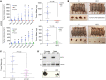
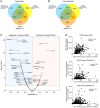
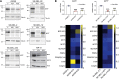
Cutaneous melanoma remains the most lethal skin cancer, and ranks third among all malignancies in terms of years of life lost. Despite the advent of immune checkpoint and targeted therapies, only roughly half of patients with advanced melanoma achieve a durable remission. Sirtuin 5 (SIRT5) is a member of the sirtuin family of protein deacylases that regulates metabolism and other biological processes. Germline Sirt5 deficiency is associated with mild phenotypes in mice. Here we showed that SIRT5 was required for proliferation and survival across all cutaneous melanoma genotypes tested, as well as uveal melanoma, a genetically distinct melanoma subtype that arises in the eye and is incurable once metastatic. Likewise, SIRT5 was required for efficient tumor formation by melanoma xenografts and in an autochthonous mouse Braf Pten-driven melanoma model. Via metabolite and transcriptomic analyses, we found that SIRT5 was required to maintain histone acetylation and methylation levels in melanoma cells, thereby promoting proper gene expression. SIRT5-dependent genes notably included MITF, a key lineage-specific survival oncogene in melanoma, and the c-MYC proto-oncogene. SIRT5 may represent a druggable genotype-independent addiction in melanoma.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cell Biology; Melanoma; Metabolism; Molecular biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Dharmadhikari N, et al. Oncolytic virus immunotherapy for melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2015;16(3):326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AG000114/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007853/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA128814/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000114/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM113900/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA216101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM101171/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007197/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007517/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007544/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK097153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA217141/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA030199/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM132261/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009676/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244931/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

