Neural oscillations are a start toward understanding brain activity rather than the end
- PMID: 33945528
- PMCID: PMC8121326
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001234
Neural oscillations are a start toward understanding brain activity rather than the end
Abstract
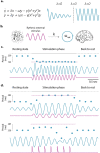
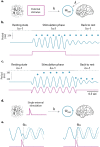
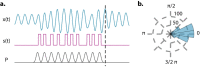
Does rhythmic neural activity merely echo the rhythmic features of the environment, or does it reflect a fundamental computational mechanism of the brain? This debate has generated a series of clever experimental studies attempting to find an answer. Here, we argue that the field has been obstructed by predictions of oscillators that are based more on intuition rather than biophysical models compatible with the observed phenomena. What follows is a series of cautionary examples that serve as reminders to ground our hypotheses in well-developed theories of oscillatory behavior put forth by theoretical study of dynamical systems. Ultimately, our hope is that this exercise will push the field to concern itself less with the vague question of "oscillation or not" and more with specific biophysical models that can be readily tested.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Comment in
-
Oscillation or not-Why we can and need to know (commentary on Doelling and Assaneo, 2021).Eur J Neurosci. 2022 Jan;55(1):201-204. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15542. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Eur J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34817088 No abstract available.
References
-
- Huygens C. lettre à son père, in øeuvres complètes de christiaan huygens, 1665. Société Holl Sci. 1893;5:243–4.
-
- Graf RF. Modern Dictionary of Electronics. Elsevier Science; 1999. p. 884.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

