Scale-up of antiretroviral treatment access among people living with HIV in Rivers State, Nigeria, 2019--2020
- PMID: 33946087
- PMCID: PMC8366506
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002858
Scale-up of antiretroviral treatment access among people living with HIV in Rivers State, Nigeria, 2019--2020
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to describe and evaluate the impact of the programme intervention of the Rivers State Antiretroviral Treatment (ART) Surge, a collaboration between the US President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) and the State Ministry of Health, to increase HIV case-finding and ART access in Rivers State, the state with the largest ART gap among people living with HIV (PWH) in Nigeria.
Design: During April 2019-September 2020, the intervention included six specific strategies: using local government area-level ART gap analysis to guide case-finding; expanding targeted community testing; tailoring comprehensive key population HIV services; engaging HIV treatment programme stakeholders; synchronizing team efforts; and using near real-time data for programme action.
Methods: Weekly reported facility and community data on tests conducted, PWH diagnosed, and PWH initiated on ART were aggregated. The total number of PWH maintained on ART was reported quarterly.
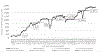
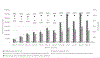
Results: During May 2019-September 2020, the weekly number of newly diagnosed PWH initiated on ART supported by PEPFAR in Rivers State increased from 82 to 1723. During October 2019-September 2020, the monthly number of people screened for HIV testing eligibility in the community increased from 44 000 to 360 000. During April 2019-September 2020, the total number of PWH on ART supported by PEPFAR statewide increased by 3.8 times, from 26 041 to 99 733.
Conclusion: The strategies applied by HIV program stakeholders contributed to scale-up of PWH identification and ART linkage within the Rivers State ART Surge. Continued gains through time indicate the importance of the application of a quality improvement approach to maintain programme flexibility and effectiveness.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS. UNAIDS country factsheets: Nigeria. 2019. https://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/nigeria. [Accessed 1 February 2021]
-
- Federal Ministry of Health Nigeria. Nigeria HIV/AIDS Indicator and Impact Survey 2018 Technical Report. Abuja, Nigeria; 2019. https://www.naiis.ng/resource/NAIIS-Report-2018.pdf. [Accessed 1 February 2021]
-
- PEPFAR. PEPFAR Panorama OU and SNU analysis: Nigeria, 2020. Washington, DC; 2020. https://pepfar-panorama.org/PEPFARLanding/#main. [Accessed 10 June 2020]
-
- Heiby J. The use of modern quality improvement approaches to strengthen African health systems: a 5-year agenda. Int J Qual Healthcare 2014; 26:117–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

