Validation of a Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Method for the Measurement of the Redox State Metabolic Ratios Lactate/Pyruvate and β-Hydroxybutyrate/Acetoacetate in Biological Samples
- PMID: 33946157
- PMCID: PMC8125771
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094752
Validation of a Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Method for the Measurement of the Redox State Metabolic Ratios Lactate/Pyruvate and β-Hydroxybutyrate/Acetoacetate in Biological Samples
Abstract
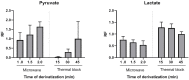
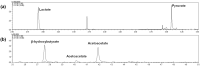
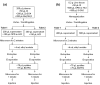
The metabolic ratios lactate/pyruvate and β-hydroxybutyrate/acetoacetate are considered valuable tools to evaluate the in vivo redox cellular state by estimating the free NAD+/NADH in cytoplasm and mitochondria, respectively. The aim of the current study was to validate a gas-chromatography mass spectrometry method for simultaneous determination of the four metabolites in plasma and liver tissue. The procedure included an o-phenylenediamine microwave-assisted derivatization, followed by liquid-liquid extraction with ethyl acetate and silylation with bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide:trimethylchlorosilane 99:1. The calibration curves presented acceptable linearity, with a limit of quantification of 0.001 mM for pyruvate, β-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate and of 0.01 mM for lactate. The intra-day and inter-day accuracy and precision were within the European Medicines Agency's Guideline specifications. No significant differences were observed in the slope coefficient of three-point standard metabolite-spiked curves in plasma or liver and water, and acceptable recoveries were obtained in the metabolite-spiked samples. Applicability of the method was tested in precision-cut liver rat slices and also in HepG2 cells incubated under different experimental conditions challenging the redox state. In conclusion, the validated method presented good sensitivity, specificity and reproducibility in the quantification of lactate/pyruvate and β-hydroxybutyrate/acetate metabolites and may be useful in the evaluation of in vivo redox states.
Keywords: GC-MS; ketone bodies; microwave-assisted derivatization; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; redox state.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Habarou F., Brassier A., Rio M., Chrétien D., Monnot S., Barbier V., Barouki R., Bonnefont J.P., Boddaert N., Chadefaux-Vekemans B., et al. Pyruvate Carboxylase Deficiency: An Underestimated Cause of Lactic Acidosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2015;2:25–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2014.11.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

