Cobalt Regulates Activation of Camk2α in Neurons by Influencing Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase 2 Quaternary Structure and Subcellular Localization
- PMID: 33946543
- PMCID: PMC8125063
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094800
Cobalt Regulates Activation of Camk2α in Neurons by Influencing Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase 2 Quaternary Structure and Subcellular Localization
Abstract
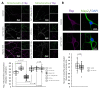
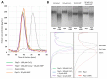
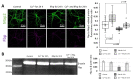
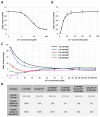
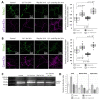
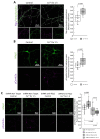
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase 2 (Fbp2) is a gluconeogenic enzyme and multifunctional protein modulating mitochondrial function and synaptic plasticity via protein-protein interactions. The ability of Fbp2 to bind to its cellular partners depends on a quaternary arrangement of the protein. NAD+ and AMP stabilize an inactive T-state of Fbp2 and thus, affect these interactions. However, more subtle structural changes evoked by the binding of catalytic cations may also change the affinity of Fbp2 to its cellular partners. In this report, we demonstrate that Fbp2 interacts with Co2+, a cation which in excessive concentrations, causes pathologies of the central nervous system and which has been shown to provoke the octal-like events in hippocampal slices. We describe for the first time the kinetics of Fbp2 in the presence of Co2+, and we provide a line of evidence that Co2+ blocks the AMP-induced transition of Fbp2 to the canonical T-state triggering instead of a new, non-canonical T-state. In such a state, Fbp2 is still partially active and may interact with its binding partners e.g., Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 2α (Camk2α). The Fbp2-Camk2α complex seems to be restricted to mitochondria membrane and it facilitates the Camk2α autoactivation and thus, synaptic plasticity.
Keywords: Fbp2; mitochondria; moonlighting protein; protein-protein interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuronal extracellular vesicles influence the expression, degradation and oligomeric state of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase 2 in astrocytes affecting their glycolytic capacity.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 9;14(1):20932. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71560-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39251668 Free PMC article.
-
Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphatase 2 Plays a Crucial Role in the Induction and Maintenance of Long-Term Potentiation.Cells. 2020 Jun 1;9(6):1375. doi: 10.3390/cells9061375. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32492972 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in quaternary structure of muscle fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase regulate affinity of the enzyme to mitochondria.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;48:55-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.12.015. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24412565
-
The Roles of Calmodulin and CaMKII in Cx36 Plasticity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 25;22(9):4473. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094473. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33922931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimulation-induced changes in diffusion and structure of calmodulin and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II proteins in neurons.Neurosci Res. 2018 Nov;136:13-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Neurosci Res. 2018. PMID: 29395358 Review.
Cited by
-
The Highly Conserved Cys95 Residue of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase 1 Mediates the pH-Driven Structure and Activity of the Enzyme and Photosynthesis.Plant Cell Environ. 2025 Sep;48(9):6941-6951. doi: 10.1111/pce.15667. Epub 2025 Jun 8. Plant Cell Environ. 2025. PMID: 40485148 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal extracellular vesicles influence the expression, degradation and oligomeric state of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase 2 in astrocytes affecting their glycolytic capacity.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 9;14(1):20932. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71560-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39251668 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial of the Special Issue "Neurobiological Mechanisms Implicated in Stress-Related Psychiatric Disorders".Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7856. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097856. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175565 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

