Preclinical Assessment Addressing Intravenous Administration of a [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-617 Microemulsion: Acute In Vivo Toxicity, Tolerability, PET Imaging, and Biodistribution
- PMID: 33946599
- PMCID: PMC8124668
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26092650
Preclinical Assessment Addressing Intravenous Administration of a [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-617 Microemulsion: Acute In Vivo Toxicity, Tolerability, PET Imaging, and Biodistribution
Abstract
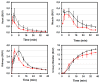
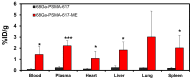
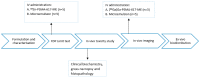
It has been herein presented that a microemulsion, known to be an effective and safe drug delivery system following intravenous administration, can be loaded with traces of [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-617 without losing its properties or causing toxicity. Following tolerated IV injections the capability of the microemulsion in altering [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-617 distribution was presented at 120 min post injection based on its ex vivo biodistribution results.
Keywords: 68Ga; PSMA-617; [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-617-ME; biodistribution; in vivo; microPET/CT; microemulsion; prostate cancer; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Muzaffar F., Singh U.K., Chauhan L. Review on microemulsion as futuristic drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013;5:39–53.
-
- Bhattacharya R., Mukhopadhyay S., Kothiyal P. Review on microemulsion—As a potential novel drug delivery system. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016;5:700–729.
-
- Mehta D.P., Rathod H.J., Shah D.P. Microemulsions: A potential novel drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharma Drug Dev. 2016;1:37–47.
-
- Nirmala M.J., Nagarajan R. Microemulsions as Potent Drug Delivery Systems. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2016;7:7439.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

