A Novel Method for COVID-19 Diagnosis Using Artificial Intelligence in Chest X-ray Images
- PMID: 33946809
- PMCID: PMC8145061
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9050522
A Novel Method for COVID-19 Diagnosis Using Artificial Intelligence in Chest X-ray Images
Abstract
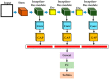
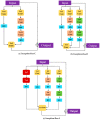
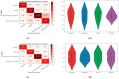
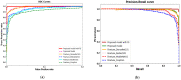
The Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease spreading rapidly and uncontrollably throughout the world. The critical challenge is the rapid detection of Coronavirus infected people. The available techniques being utilized are body-temperature measurement, along with anterior nasal swab analysis. However, taking nasal swabs and lab testing are complex, intrusive, and require many resources. Furthermore, the lack of test kits to meet the exceeding cases is also a major limitation. The current challenge is to develop some technology to non-intrusively detect the suspected Coronavirus patients through Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques such as deep learning (DL). Another challenge to conduct the research on this area is the difficulty of obtaining the dataset due to a limited number of patients giving their consent to participate in the research study. Looking at the efficacy of AI in healthcare systems, it is a great challenge for the researchers to develop an AI algorithm that can help health professionals and government officials automatically identify and isolate people with Coronavirus symptoms. Hence, this paper proposes a novel method CoVIRNet (COVID Inception-ResNet model), which utilizes the chest X-rays to diagnose the COVID-19 patients automatically. The proposed algorithm has different inception residual blocks that cater to information by using different depths feature maps at different scales, with the various layers. The features are concatenated at each proposed classification block, using the average-pooling layer, and concatenated features are passed to the fully connected layer. The efficient proposed deep-learning blocks used different regularization techniques to minimize the overfitting due to the small COVID-19 dataset. The multiscale features are extracted at different levels of the proposed deep-learning model and then embedded into various machine-learning models to validate the combination of deep-learning and machine-learning models. The proposed CoVIR-Net model achieved 95.7% accuracy, and the CoVIR-Net feature extractor with random-forest classifier produced 97.29% accuracy, which is the highest, as compared to existing state-of-the-art deep-learning methods. The proposed model would be an automatic solution for the assessment and classification of COVID-19. We predict that the proposed method will demonstrate an outstanding performance as compared to the state-of-the-art techniques being used currently.
Keywords: chest X-ray images; data analytics; feature extraction; healthcare; image processing; pandemic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







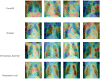
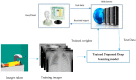
Similar articles
-
LCSB-inception: Reliable and effective light-chroma separated branches for Covid-19 detection from chest X-ray images.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Nov;150:106195. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106195. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 37859288 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and Accurate Detection of COVID-19 Along With 14 Other Chest Pathologies Using a Multi-Level Classification: Algorithm Development and Validation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Feb 10;23(2):e23693. doi: 10.2196/23693. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33529154 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosing Covid-19 chest x-rays with a lightweight truncated DenseNet with partial layer freezing and feature fusion.Biomed Signal Process Control. 2021 Jul;68:102583. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102583. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2021. PMID: 33828610 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis of COVID-19 Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning: A Review.Curr Med Imaging. 2021;17(12):1403-1418. doi: 10.2174/1573405617666210713113439. Curr Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34259149 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence Based COVID-19 Detection and Classification Model on Chest X-ray Images.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Apr 22;11(9):1204. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11091204. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37174746 Free PMC article.
-
Automated COVID-19 Classification Using Heap-Based Optimization with the Deep Transfer Learning Model.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Aug 22;2022:7508836. doi: 10.1155/2022/7508836. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Aug 9;2023:9843718. doi: 10.1155/2023/9843718. PMID: 36045956 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Investigating the performance of machine learning algorithms in predicting the survival of COVID-19 patients: A cross section study of Iran.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 13;6(4):e1212. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1212. eCollection 2023 Apr. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37064314 Free PMC article.
-
The use of artificial intelligence for delivery of essential health services across WHO regions: a scoping review.Front Public Health. 2023 Jul 4;11:1102185. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1102185. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37469694 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning Assisted Rapid Diagnosis of COVID-19 from Chest Radiographical Images: A Survey.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Oct 12;2022:1306664. doi: 10.1155/2022/1306664. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36304775 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization, Coronavirus 2020. [(accessed on 10 July 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1.
-
- Wuhan Municipal Health Commission, Report on Unexplained Viral Pneumonia. [(accessed on 25 January 2020)]; Available online: http://wjw.wuhan.gov.cn/front/web/showDetail/2020010509020.
-
- Coronavirus Symptoms and How to Protect Yourself: What We Know 2020. [(accessed on 12 July 2020)]; Available online: https://www.wsj.com/articles/what-we-know-about-the-coronavirus-11579716....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

