Effectiveness of N-Acetylcysteine in the Treatment of Renal Deterioration Caused by Long-Term Exposure to Bisphenol A
- PMID: 33946939
- PMCID: PMC8145636
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11050655
Effectiveness of N-Acetylcysteine in the Treatment of Renal Deterioration Caused by Long-Term Exposure to Bisphenol A
Erratum in
-
Correction: Kobroob et al. Effectiveness of N-Acetylcysteine in the Treatment of Renal Deterioration Caused by Long-Term Exposure to Bisphenol A. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 655.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 12;13(12):1781. doi: 10.3390/biom13121781. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136679 Free PMC article.
Abstract
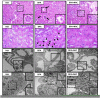
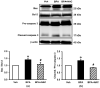
Human health hazards caused by bisphenol A (BPA), a precursor for epoxy resins and polycarbonate-based plastics, are well documented and are closely associated with mitochondrial impairment and oxidative imbalance. This study aimed to assess the therapeutic efficacy of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on renal deterioration caused by long-term BPA exposure and examine the signaling transduction pathway involved. Male Wistar rats were given vehicle or BPA orally for 12 weeks then the BPA-treated group was subdivided to receive vehicle or NAC concurrently with BPA for a further 4 weeks, while the vehicle-treated normal control group continued to receive vehicle through to the end of experiment. Proteinuria, azotemia, glomerular filtration reduction and histopathological abnormalities caused by chronic BPA exposure were significantly reduced following NAC therapy. NAC also diminished nitric oxide and lipid peroxidation but enhanced renal glutathione levels, and counteracted BPA-induced mitochondrial swelling, increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production, and the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. The benefit of NAC was related to the modulation of signaling proteins in the AMPK-SIRT3-SOD2 axis. The present study shows the potential of NAC to restore mitochondrial integrity and oxidative balance after long-term BPA exposure, and suggests that NAC therapy is an effective approach to tackle renal deterioration in this condition.
Keywords: N-acetylcysteine; bisphenol A; kidney; long-term exposure; mitochondria; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


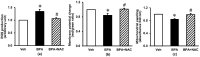

Comment in
-
Comment on Kobroob et al. Effectiveness of N-Acetylcysteine in the Treatment of Renal Deterioration Caused by Long-Term Exposure to Bisphenol A. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 655.Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 15;11(6):888. doi: 10.3390/biom11060888. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34203790 Free PMC article.
-
New Evidence of Renal and Cardiovascular Alterations Promoted by Bisphenol A.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 8;11(11):1649. doi: 10.3390/biom11111649. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carchia E., Porreca I., Almeida P.J., D’Angelo F., Cuomo D., Ceccarelli M., De Felice M., Mallardo M., Ambrosino C. Evaluation of low doses BPA-induced perturbation of glycemia by toxicogenomics points to a primary role of pancreatic islets and to the mechanism of toxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1959. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.319. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

