A Review on Properties and Application of Bio-Based Poly(Butylene Succinate)
- PMID: 33946989
- PMCID: PMC8125033
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13091436
A Review on Properties and Application of Bio-Based Poly(Butylene Succinate)
Abstract
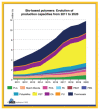
Researchers and companies have increasingly been drawn to biodegradable polymers and composites because of their environmental resilience, eco-friendliness, and suitability for a range of applications. For various uses, biodegradable fabrics use biodegradable polymers or natural fibers as reinforcement. Many approaches have been taken to achieve better compatibility for tailored and improved material properties. In this article, PBS (polybutylene succinate) was chosen as the main topic due to its excellent properties and intensive interest among industrial and researchers. PBS is an environmentally safe biopolymer that has some special properties, such as good clarity and processability, a shiny look, and flexibility, but it also has some drawbacks, such as brittleness. PBS-based natural fiber composites are completely biodegradable and have strong physical properties. Several research studies on PBS-based composites have been published, including physical, mechanical, and thermal assessments of the properties and its ability to replace petroleum-based materials, but no systematic analysis of up-to-date research evidence is currently available in the literature. The aim of this analysis is to highlight recent developments in PBS research and production, as well as its natural fiber composites. The current research efforts focus on the synthesis, copolymers and biodegradability for its properties, trends, challenges and prospects in the field of PBS and its composites also reviewed in this paper.
Keywords: biodegradability; copolymers; mechanical; physical properties; poly butylene succinate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures















References
-
- Chidambarampadmavathy K., Karthikeyan O.P., Heimann K. Sustainable bio-plastic production through landfill methane recycling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017;71:555–562. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.083. - DOI
-
- Gourmelon G. Global plastic production rises, recycling lags—New worldwatch Institute analysis explores trends in global plastic consumption and recycling. Worldwatch Inst. 2015;22:91–95.
-
- Mazhandu Z.S., Muzenda E., Mamvura T.A., Belaid M. Integrated and Consolidated Review of Plastic Waste Management and Bio-Based Biodegradable Plastics: Challenges and Opportunities. Sustainability. 2020;12:8360. doi: 10.3390/su12208360. - DOI
-
- Zhang F., Zhao Y., Wang D., Yan M., Zhang J., Zhang P., Chen C. Current technologies for plastic waste treatment: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020;282:124523. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124523. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

