Complications of thoracoscopic talc insufflation for the treatment of malignant pleural effusions: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 33947423
- PMCID: PMC8097876
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-021-01475-1
Complications of thoracoscopic talc insufflation for the treatment of malignant pleural effusions: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Talc pleurodesis is an effective treatment for malignant pleural effusions (MPEs). This study was designed to estimate complication rates of thoracoscopic talc insufflation.
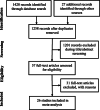
Methods: Literature search was conducted in electronic databases and studies were selected if they reported complication rates of thoracoscopic talc insufflation in cancer patients with MPEs. Meta-analyses of proportions were performed to obtain incidence rates of complications.
Results: Twenty-six studies (4482 patients; age 62.9 years [95% confidence interval (CI): 61.5, 64.4]; 50% [95% CI: 43, 58] females) were included. Intraoperative, perioperative, 30-day, and 90-day mortality rates were 0% [95% CI: 0, 1], 2% [95% CI: 0, 4], 7% [95% CI: 3, 13] and 21% [95% CI: 5, 43] respectively. Incidence rates [95% CI] of various complications were: pain (20% [1, 2]), fever (14% [3, 4]), dyspnea (13% [5, 6]), pneumothorax (6% [7, 8]) pneumonia (4% [0, 12]), emphysema (3% [3, 7]), prolonged air leakage (3% [0, 7]), prolonged drainage (3% [9, 10]), thromboembolism (3% [9, 11]), lung injury (2% [7, 12]), respiratory insufficiency (2% [0, 5]), re-expansion pulmonary edema (1% [0, 3]), empyema (1% [0, 2]), respiratory failure (0% [0, 1]), and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS; 0% [0, 1].
Conclusions: Whereas pain and fever were the most frequent complications of thoracoscopic talc insufflation, the incidence of ARDS was low. Pneumothorax, pneumonia, emphysema, prolonged air leakage, pulmonary embolism, arrythmia, re-expansion pulmonary edema, and empyema are important complications of thoracoscopic talc insufflation.
Keywords: Malignant pleural effusions; Pleurodesis; Talc insufflation; Thoracoscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thoracoscopy talc poudrage : a 15-year experience.Chest. 2001 Mar;119(3):801-6. doi: 10.1378/chest.119.3.801. Chest. 2001. PMID: 11243960
-
Talc pleurodesis: comparison of talc slurry instillation with thoracoscopic talc insufflation for malignant pleural effusions.J BUON. 2006 Oct-Dec;11(4):463-7. J BUON. 2006. PMID: 17309178
-
Lung injury following thoracoscopic talc insufflation: experience of a single North American center.Chest. 2010 Jun;137(6):1375-81. doi: 10.1378/chest.09-2020. Epub 2010 Jan 22. Chest. 2010. PMID: 20097802
-
Talc slurry versus thoracoscopic talc insufflation for malignant pleural effusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Bras Pneumol. 2024 Aug 19;50(3):e20240115. doi: 10.36416/1806-3756/e20240115. eCollection 2024. J Bras Pneumol. 2024. PMID: 39166590 Free PMC article.
-
[Talc pleurodesis in malignant pleural effusions].Pneumologie. 2006 Feb;60(2):89-95. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-919139. Pneumologie. 2006. PMID: 16463249 Review. German.
Cited by
-
A Case of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Following Pleurodesis With Talc.Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2023 Apr 24;16:11795476231170196. doi: 10.1177/11795476231170196. eCollection 2023. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37124843 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the efficacy and advancements of medical pleurodesis: a comprehensive review of current research.Breathe (Sheff). 2024 Aug 27;20(2):240002. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0002-2024. eCollection 2024 Jun. Breathe (Sheff). 2024. PMID: 39193457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New strategies in the management of pneumothorax.Breathe (Sheff). 2025 Aug 19;21(3):240250. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0250-2024. eCollection 2025 Jul. Breathe (Sheff). 2025. PMID: 40837422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond diagnosis: a narrative review of the evolving therapeutic role of medical thoracoscopy in the management of pleural diseases.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Mar 29;16(3):2177-2195. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1745. Epub 2024 Mar 27. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 38617786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Talc-induced pericardial granulomatosis after recurrent pleurodesis: a rare cause of incessant pericarditis-case report.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2024 Nov 14;8(12):ytae603. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytae603. eCollection 2024 Dec. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39619724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antony VB, Jantz MA. Pleural effusions. Malignant Pleural Effusions. Encyclopedia Respir Med. 2006; 10.1016/B0-12-370879-6/00304-5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

