Convalescent plasma for adults with acute COVID-19 respiratory illness (CONCOR-1): study protocol for an international, multicentre, randomized, open-label trial
- PMID: 33947446
- PMCID: PMC8094980
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-021-05235-3
Convalescent plasma for adults with acute COVID-19 respiratory illness (CONCOR-1): study protocol for an international, multicentre, randomized, open-label trial
Abstract
Background: Convalescent plasma has been used for numerous viral diseases including influenza, severe acute respiratory syndrome, Middle East respiratory syndrome and Ebola virus; however, evidence to support its use is weak. SARS-CoV-2 is a novel coronavirus responsible for the 2019 global pandemic of COVID-19 community acquired pneumonia. We have undertaken a randomized controlled trial to assess the efficacy and safety of COVID-19 convalescent plasma (CCP) in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
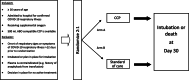
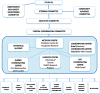
Methods: CONCOR-1 is an open-label, multicentre, randomized trial. Inclusion criteria include the following: patients > 16 years, admitted to hospital with COVID-19 infection, receiving supplemental oxygen for respiratory complications of COVID-19, and availability of blood group compatible CCP. Exclusion criteria are : onset of respiratory symptoms more than 12 days prior to randomization, intubated or imminent plan for intubation, and previous severe reactions to plasma. Consenting patients are randomized 2:1 to receive either approximately 500 mL of CCP or standard of care. CCP is collected from donors who have recovered from COVID-19 and who have detectable anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies quantified serologically. The primary outcome is intubation or death at day 30. Secondary outcomes include ventilator-free days, length of stay in intensive care or hospital, transfusion reactions, serious adverse events, and reduction in SARS-CoV-2 viral load. Exploratory analyses include patients who received CCP containing high titre antibodies. A sample size of 1200 patients gives 80% power to detect a 25% relative risk reduction assuming a 30% baseline risk of intubation or death at 30 days (two-sided test; α = 0.05). An interim analysis and sample size re-estimation will be done by an unblinded independent biostatistician after primary outcome data are available for 50% of the target recruitment (n = 600).
Discussion: This trial will determine whether CCP will reduce intubation or death non-intubated adults with COVID-19. The trial will also provide information on the role of and thresholds for SARS-CoV-2 antibody titres and neutralization assays for donor qualification.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT04348656 . Registered on 16 April 2020.
Keywords: COVID-19; Convalescent plasma; Coronavirus; Randomized controlled trial; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Worldometers. COVID-19 Coronovirus Pandemic. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/. Accessed 18 May 2020.
-
- Shen C, Wang Z, Zhao F, Yang Y, Li J, Yuan J, Wang F, Li D, Yang M, Xing L, Wei J, Xiao H, Yang Y, Qu J, Qing L, Chen L, Xu Z, Peng L, Li Y, Zheng H, Chen F, Huang K, Jiang Y, Liu D, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Liu L. Treatment of 5 critically ill patients with COVID-19 with convalescent plasma. JAMA. 2020;323(16):1582–1589. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4783. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 447352/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- n/a/Ontario Research Fund
- n/a/University of Toronto COVID-19 Action Initiative
- n/a/Academic Health Science Centre Alternative Funding Plan
- n/a/Ministère de l'Économie et de l'Innovation (Quebec)
- n/a/Ministry of Health (Saskatchewan)
- n/a/Sunnybrook Hospital Foundation
- n/a/Hamilton Academic Health Sciences Organization
- n/a/University of Alberta Hospital Foundation
- n/a/McMaster University
- n/a/University Health Network- Emergent Access to Innovation Funds
- n/a/Fondations CHU Sainte-Justine (CA)
- n/a/Sinai Health System Foundation
- n/a/The Ottawa Hospital Academic Medical Organization
- n/a/The Ottawa Hospital Foundation COVID-19 Research Fund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

