atpD gene sequencing, multidrug resistance traits, virulence-determinants, and antimicrobial resistance genes of emerging XDR and MDR-Proteus mirabilis
- PMID: 33947875
- PMCID: PMC8096940
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-88861-w
atpD gene sequencing, multidrug resistance traits, virulence-determinants, and antimicrobial resistance genes of emerging XDR and MDR-Proteus mirabilis
Abstract
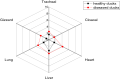
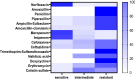
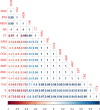
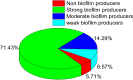
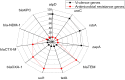
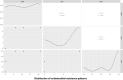
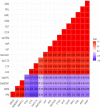
Proteus mirabilis is a common opportunistic pathogen causing severe illness in humans and animals. To determine the prevalence, antibiogram, biofilm-formation, screening of virulence, and antimicrobial resistance genes in P. mirabilis isolates from ducks; 240 samples were obtained from apparently healthy and diseased ducks from private farms in Port-Said Province, Egypt. The collected samples were examined bacteriologically, and then the recovered isolates were tested for atpD gene sequencing, antimicrobial susceptibility, biofilm-formation, PCR detection of virulence, and antimicrobial resistance genes. The prevalence of P. mirabilis in the examined samples was 14.6% (35/240). The identification of the recovered isolates was confirmed by the atpD gene sequencing, where the tested isolates shared a common ancestor. Besides, 94.3% of P. mirabilis isolates were biofilm producers. The recovered isolates were resistant to penicillins, sulfonamides, β-Lactam-β-lactamase-inhibitor-combinations, tetracyclines, cephalosporins, macrolides, and quinolones. Using PCR, the retrieved strains harbored atpD, ureC, rsbA, and zapA virulence genes with a prevalence of 100%, 100%, 94.3%, and 91.4%, respectively. Moreover, 31.4% (11/35) of the recovered strains were XDR to 8 antimicrobial classes that harbored blaTEM, blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M, tetA, and sul1 genes. Besides, 22.8% (8/35) of the tested strains were MDR to 3 antimicrobial classes and possessed blaTEM, tetA, and sul1genes. Furthermore, 17.1% (6/35) of the tested strains were MDR to 7 antimicrobial classes and harbored blaTEM, blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M, tetA, and sul1 genes. Alarmingly, three strains were carbapenem-resistant that exhibited PDR to all the tested 10 antimicrobial classes and shared blaTEM, blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M, tetA, and sul1 genes. Of them, two strains harbored the blaNDM-1 gene, and one strain carried the blaKPC gene. In brief, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study demonstrating the emergence of XDR and MDR-P.mirabilis in ducks. Norfloxacin exhibited promising antibacterial activity against the recovered XDR and MDR-P. mirabilis. The emergence of PDR, XDR, and MDR-strains constitutes a threat alarm that indicates the complicated treatment of the infections caused by these superbugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wang Y, et al. An outbreak of Proteus mirabilis food poisoning associated with eating stewed pork balls in brown sauce, Beijing. Food Control. 2010;21:302–305. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2009.06.009. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

