The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics
- PMID: 33948025
- PMCID: PMC8387231
- DOI: 10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6
The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Sep;18(9):671. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00481-x. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34131318 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Author Correction: The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Aug;19(8):551. doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00628-4. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35538163 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
In 2019, the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) convened a panel of experts specializing in nutrition, microbial physiology, gastroenterology, paediatrics, food science and microbiology to review the definition and scope of postbiotics. The term 'postbiotics' is increasingly found in the scientific literature and on commercial products, yet is inconsistently used and lacks a clear definition. The purpose of this panel was to consider the scientific, commercial and regulatory parameters encompassing this emerging term, propose a useful definition and thereby establish a foundation for future developments. The panel defined a postbiotic as a "preparation of inanimate microorganisms and/or their components that confers a health benefit on the host". Effective postbiotics must contain inactivated microbial cells or cell components, with or without metabolites, that contribute to observed health benefits. The panel also discussed existing evidence of health-promoting effects of postbiotics, potential mechanisms of action, levels of evidence required to meet the stated definition, safety and implications for stakeholders. The panel determined that a definition of postbiotics is useful so that scientists, clinical triallists, industry, regulators and consumers have common ground for future activity in this area. A generally accepted definition will hopefully lead to regulatory clarity and promote innovation and the development of new postbiotic products.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.S. serves on the board of ISAPP, is a board member of Yoghurt in Nutrition Initiative and has been a speaker in meetings funded by industry, Nestlé Nutrition Institute and Institute Danone. M.C.C. has participated as a speaker for HIPP, Danone, Nutricia, Nestlé Nutrition Institute and Mead Johnson. A.E. has led industry-sponsored research projects with support from B Food Science and Takanashi Milk Products, and has been a speaker for the companies. C.H. serves on the board of ISAPP, is a consultant to Artugen Therapeutics developing a live biotherapeutic, and has received research grants from several industry partners, including ADARE Pharmaceuticals, manufacturers of Lacteol. S.L. serves on the academic board of ISAPP and has received research grants from several industry partners, such as Yun. She has been compensated for speaking by Yakult. E.M.M.Q. serves on the board of ISAPP, as a consultant to 4D Pharma, Alimentary Health, Allergan, Biocodex, Ironwood, Salix, Takeda and Vibrant, and has research support from 4D Pharma, Biomerica and Vibrant. M.E.S. has been compensated for speaking engagements or for consulting from Associated British Foods, California Dairy Research Foundation, Cargill, Danone Research, Danone USA, Fairlife, General Mills, GlaxoSmithKline, JJ Heimbach, Kellogg, Kerry, Mead Johnson, Medscape, PepsiCo, Pfizer, Probi, Procter & Gamble, Sanofi, Trouw Nutrition, Visalia Dairy Company, Winclove Probiotics and Yakult. R.S. has participated as a clinical investigator, and/or advisory board member, and/or consultant, and/or speaker for Abbott, Danone and Nestlé. J.R.S. has led industry-sponsored research projects with support from AstraZeneca, Danone, Servier and Vitacress. H.S. serves on the board of ISAPP and has participated as a clinical investigator, and/or advisory board member, and/or consultant, and/or speaker for Arla, Biogaia, Biocodex, Ch. Hansen, Danone, Nestlé, Nestlé Nutrition Institute, Nutricia and Merck. G.V. has led industry-sponsored research projects on dairy products and probiotics. These projects were independently carried out and had no influence on the content of this manuscript. He is member of the Argentinian board of the Yoghurt in Nutrition Initiative (YINI Danone Argentina) and serves on the board of ISAPP. He was not a member of ISAPP Board at the time of the meeting, but has been elected as a board member as of June 2020.
Figures
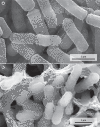
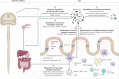
Comment in
-
Reply to: Postbiotics - when simplification fails to clarify.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Nov;18(11):827-828. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00522-5. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34556824 No abstract available.
-
Postbiotics - when simplification fails to clarify.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Nov;18(11):825-826. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00521-6. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34556825 No abstract available.
References
-
- Selma-Royo M, et al. Shaping microbiota during the first 1000 days of life. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019;1125:3–24. - PubMed
-
- Hill C, et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014;11:506–514. - PubMed
-
- Gibson GR, et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017;14:491–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

