Testing at scale during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 33948037
- PMCID: PMC8094986
- DOI: 10.1038/s41576-021-00360-w
Testing at scale during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Assembly and publication of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) genome in January 2020 enabled the immediate development of tests to detect the new virus. This began the largest global testing programme in history, in which hundreds of millions of individuals have been tested to date. The unprecedented scale of testing has driven innovation in the strategies, technologies and concepts that govern testing in public health. This Review describes the changing role of testing during the COVID-19 pandemic, including the use of genomic surveillance to track SARS-CoV-2 transmission around the world, the use of contact tracing to contain disease outbreaks and testing for the presence of the virus circulating in the environment. Despite these efforts, widespread community transmission has become entrenched in many countries and has required the testing of populations to identify and isolate infected individuals, many of whom are asymptomatic. The diagnostic and epidemiological principles that underpin such population-scale testing are also considered, as are the high-throughput and point-of-care technologies that make testing feasible on a massive scale.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
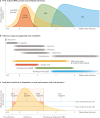

References
-
- Sheridan C. Coronavirus and the race to distribute reliable diagnostics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020;38:382–384. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Molecular assays to diagnose COVID-19: summary table of available protocols. WHOhttps://www.who.int/publications/m/item/molecular-assays-to-diagnose-cov... (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

