Endoscopic management of benign recalcitrant esophageal strictures
- PMID: 33948052
- PMCID: PMC8079876
- DOI: 10.20524/aog.2021.0585
Endoscopic management of benign recalcitrant esophageal strictures
Abstract
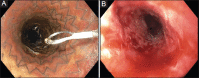
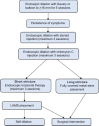
Benign esophageal strictures are one of the common clinical conditions managed by endoscopists. Nearly 90% of the benign esophageal strictures respond to endoscopic dilation. However, a small percentage of patients progress to recalcitrant strictures. The benign recalcitrant esophageal strictures are difficult to manage both medically and endoscopically as they do not respond to conventional treatment with proton pump inhibitors and esophageal dilations. Patients with benign recalcitrant esophageal strictures are at a high risk of developing debilitating malnutrition and morbidity due to severe dysphagia. This condition is associated with psychological trauma to patients as treatments are usually prolonged with poor outcomes. Also, this can be a financial burden on the healthcare industry due to several sessions of treatment. In this article, we discuss the classification of benign esophageal strictures, evidence-based treatment strategies, endoscopic procedural techniques, and complications of endoscopic interventions. We aim to guide providers in managing benign esophageal strictures with a focus on endoscopic management of benign recalcitrant esophageal strictures.
Keywords: Benign recalcitrant esophageal strictures; IT knife; esophageal stent; intralesional steroid injection; mitomycin C.
Copyright: © 2021 Hellenic Society of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None
Figures
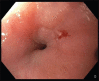
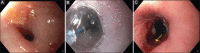
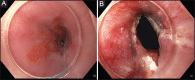
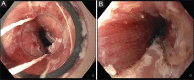
References
-
- Dryden GW, McClave SA. Methods of treating dysphagia caused by benign esophageal strictures. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;3:135–143.
-
- Pasha SF, Acosta RD, Chandrasekhara V, et al. The role of endoscopy in the evaluation and management of dysphagia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79:191–201. - PubMed
-
- Siersema PD. Treatment options for esophageal strictures. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;5:142–152. - PubMed
-
- Mullick T, Falk GW. Esophageal strictures:etiology and diagnosis. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;3:128–134.
-
- Castell DO, Donner MW. Evaluation of dysphagia:a careful history is crucial. Dysphagia. 1987;2:65–71. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
