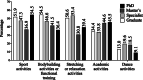Using distance learning as a strategy for maintaining income of Physical Education professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 33948103
- PMCID: PMC8084588
- DOI: 10.1007/s10639-021-10545-9
Using distance learning as a strategy for maintaining income of Physical Education professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
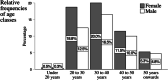
The period of social distancing caused by the COVID-19 pandemic is characterized as an effective proposal to control the spread of the coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), however, it changes the social dynamics of individuals in society. Based on this question, the present study aimed to understand how was the performance of Brazilian physical education professionals during this period. The sample consisted of 400 Physical Education professionals from Brazil, 224 women (56.0%) and 176 men (44.0%), selected at random, by filling out a questionnaire. Sports activities were predominant among professionals, followed by bodybuilding activities or functional training. Most professionals performed their activities at home (71%) and used different digital platforms as work tools, noting that distance learning was a strategy used and well regarded by professionals. However, even with the use of specific intervention strategies, professional income showed fluctuations during the pandemic, with academic degrees being one of the factors responsible for changing the workload.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; ELearning; Physical education and training; Quarantine.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestNo potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Agresti A, Finlay B. Métodos estatísticos para as ciências sociais. Penso Editora; 2012.
-
- Aquino, E. M. L., Silveira, I. H., Pescarini, J. M., Aquino, R., Souza-Filho, J. A. de, Rocha, A. dos S., … Lima, R. T. dos R. S. (2020). Medidas de distanciamento social no controle da pandemia de COVID-19: potenciais impactos e desafios no Brasil. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva, 25, 2423–2446. 10.1590/1413-81232020256.1.10502020. - PubMed
-
- Bastos, S. B., & Cajueiro, D. O. (2020). Modeling and forecasting the early evolution of the Covid-19 pandemic in Brazil. arXiv preprint. Available in: https://covid-19.conacyt.mx/jspui/handle/1000/4048. Accessed 30 March 2020. - PMC - PubMed
-
- BBC. (2020). Coronavirus confirmed as pandemic by World Health Organization. Available in: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-5183994. Accessed 30 March 2020.
-
- Bezerra, A. C. V., da Silva, C. E. M., Soares, F. R. G., & da Silva, J. A. M. (2020). Fatores associados ao comportamento da população durante o isolamento social na pandemia de COVID-19. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva,25, 2411–2421. 10.1590/1413-81232020256.1.10792020. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous