Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with breast cancer brain oligometastases - molecular subtypes and clinical outcomes
- PMID: 33948296
- PMCID: PMC8086712
- DOI: 10.5603/RPOR.a2021.0001
Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with breast cancer brain oligometastases - molecular subtypes and clinical outcomes
Abstract
Background: We sought to determine the clinical outcomes of patients with breast cancer (BC) who had undergone stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for a limited number of brain metastases (BM) and to identify factors influencing overall survival (OS) and local control.
Materials and methods: The records of 45 patients who underwent SRS for 72 brain lesions were retrospectively evaluated. Statistics included the chi-squared test, Kaplan-Meier method, and the multivariate Cox model.
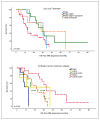
Results: The median number of treated BM was 2 (range 1-10). Median OS from BM diagnosis and post-SRS were 27.6 [95% confidence interval (CI): 14.8-40.5) and 18.5 months (95% CI: 11.1-25.8), respectively. One-year and two-year survival rates after BM diagnosis were 55% and 41%, respectively. In a univariate analysis, the Luminal-B-human-epidermal-growth-receptor-positive (HER2+) subtype had the longest median OS at 39.1 months (95% CI: 34.1-44.1, p = 0.004). In an adjusted analysis, grade 2 [hazard ratio (HR): 0.1; 95% CI: 0.1-0.6, p = 0.005), craniotomy (HR: 0.3; 95% CI: 0.1-0.7; p = 0.006), and ≥ 2 systemic therapies received (HR: 0.3; 95% CI: 0.1-0.9, p = 0.028) were associated with improved OS. One-year and two-year intracranial progression-free survival rates were 85% and 63%, respectively. Four factors for a higher risk of any intracranial recurrence remained significant in the adjusted analysis, as follows: age < 50 years (HR: 4.2; 95% CI: 1.3-36.3; p = 0.014), grade 3 (HR: 3.7; 95% CI: 1.1-13.2; p = 0.038), HER2+ (HR: 6.9; 95% CI: 1.3-36.3; p = 0.023), and whether the brain was the first metastatic site (HR: 4.7; 95% CI: 1.6-14.5; p = 0.006).
Conclusion: Intrinsic BC characteristics are important determinants for both survival and intracranial control for patients undergoing SRS for oligometastatic brain disease.
Keywords: brain metastases; breast cancer; molecular subtype; radiation therapy; stereotactic radiosurgery.
© 2021 Greater Poland Cancer Centre.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Women Older than 65 with Breast Cancer Brain Metastases.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 27;16(1):137. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010137. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201564 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role for LINAC-based stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of 5 or more radioresistant melanoma brain metastases.J Neurosurg. 2015 Nov;123(5):1261-7. doi: 10.3171/2014.12.JNS141919. Epub 2015 Jul 3. J Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 26140482
-
A matched-pair analysis comparing stereotactic radiosurgery with whole-brain radiotherapy for patients with multiple brain metastases.J Neurooncol. 2020 May;147(3):607-618. doi: 10.1007/s11060-020-03447-2. Epub 2020 Apr 1. J Neurooncol. 2020. PMID: 32239433
-
Stereotactic Cavity Irradiation or Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Following Brain Metastases Resection-Outcome, Prognostic Factors, and Recurrence Patterns.Front Oncol. 2020 May 8;10:693. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00693. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32477942 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the management of breast cancer brain metastases.Neurooncol Adv. 2021 Nov 27;3(Suppl 5):v63-v74. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdab119. eCollection 2021 Nov. Neurooncol Adv. 2021. PMID: 34859234 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improved outcomes for triple negative breast cancer brain metastases patients after stereotactic radiosurgery and new systemic approaches.J Neurooncol. 2024 May;168(1):99-109. doi: 10.1007/s11060-024-04651-0. Epub 2024 Apr 17. J Neurooncol. 2024. PMID: 38630386
-
Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Intracranial Breast Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 21;16(20):3551. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203551. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456645 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
