Outcomes of infratentorial cranial surgery for tumor resection in older patients: An analysis of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program
- PMID: 33948314
- PMCID: PMC8088538
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_25_2021
Outcomes of infratentorial cranial surgery for tumor resection in older patients: An analysis of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program
Abstract
Background: Poorer outcomes for infratentorial tumor resection have been reported. There is a lack of large multicenter analyses describing infratentorial surgery outcomes in older patients. We characterized outcomes in patients aged ≥65 years undergoing infratentorial cranial surgery.
Methods: The National Surgical Quality Improvement Project database was queried from 2012 to 2018 for patients ≥18 years undergoing elective infratentorial cranial surgery for tumor resection. Patients were grouped into 65-74 years, ≥75 years, and 18-64 years cohorts. Multivariable regressions compared outcome measures.
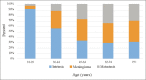
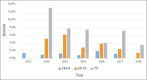
Results: Of 2212 patients, 28.3% were ≥65 years, of whom 24.8% were ≥75 years. Both older subpopulations had worse American Society of Anesthesiologists classification compared to controls (P < 0.01) and more comorbidities. Patients 65-74 and ≥75 years had higher rates of major complication (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 1.77, 95% CI = 1.13-2.79 and aOR = 3.44, 95% CI = 1.96-6.02, respectively), prolonged length of stay (LOS) (aOR = 1.89, 95% CI = 1.15-3.12 and aOR = 3.00, 95% CI = 1.65-5.44, respectively), and were more likely to be discharged to a location other than home (aOR = 2.43, 95% CI =1.73-3.4 and aOR = 3.41, 95% CI = 2.18-5.33, respectively) relative to controls. Patients ≥75 had higher rates of readmission (aOR = 1.86, 95% CI = 1.13-3.08) and mortality (aOR = 3.28, 95% CI = 1.21-8.89) at 30 days.
Conclusion: Patients ≥65 years experienced more complications, prolonged LOS, and were less often discharged home than adults <65 years. Patients ≥75 years had higher rates of 30-day readmission and mortality. There is a need for careful preoperative optimization in older patients undergoing infratentorial tumor cranial surgery.
Keywords: Brain tumor; Cranial; Elderly; Infratentorial; Meningioma.
Copyright: © 2021 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Angarita FA, Acuna SA, Cordeiro E, Elnahas A, Sutradhar S, Jackson T, et al. Thirty-day postoperative morbidity and mortality in elderly women with breast cancer: An analysis of the NSQIP database. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018;170:373–9. - PubMed
-
- Babu R, Sharma R, Karikari IO, Owens TR, Friedman AH, Adamson C. Outcome and prognostic factors in adult cerebellar glioblastoma. J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20:1117–21. - PubMed
-
- Bauman G, Fisher B, Watling C, Cairncross JG, Macdonald D. Adult supratentorial low-grade glioma: Long-term experience at a single institution. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75:1401–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources