Asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP) regulates myocardial apoptosis in response to radiation exposure via alterations in NRF2 activation
- PMID: 33948354
- PMCID: PMC8085837
Asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP) regulates myocardial apoptosis in response to radiation exposure via alterations in NRF2 activation
Abstract
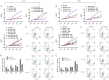
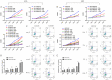
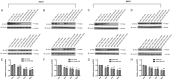
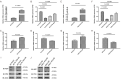
Radiation-induced heart disease (RIHD) leads to myocardial dysfunction and metabolic abnormalities in patients treated with thoracic irradiation which restricts the long-term survival benefits of radiotherapy. There is no specific or effective manner of intervention currently available. Asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP) plays a pivotal role in the maintenance of cellular functions through regulating proteolytic cleavage as peptidase enzyme. We aimed to investigate the role of unique cardiac AEP in cardiac function by modulating key signaling elements in the myocardium. The murine heart was exposed to a single dose of 14 Gy radiation. Cellular signaling and apoptosis was analyzed in human and rat cardiomyocytes treated with various doses of radiation, we observed expression of AEP was increased by immunohistochemical staining in murine heart exposed to radiation. The AEP production along with its increased level of mRNA expression was associated with increased doses of radiation (0, 2, 5, 10 Gy) in cardiomyocytes. The myocardial cells transfected with AEP overexpression showed overall cellular viability enhancement, DNA damage inhibition, the foci formation of γ-H2AX suppressed and DNA repair enhancement significantly after radiation exposure. Small interfering RNA-mediated AEP knockdown was with reduced cardiomyocyte viability, elevated apoptotic rate, increased γ-H2AX foci formation and inhibited DNA repair as well after irradiation. After radiation exposure of 10 Gy, the expression of AEP increased in P53 overexpressing cardiomyocytes and decreased in the P53 knockdown cells, indicates that radiation-induced expression of AEP might be regulated by P53. Moreover, treatments with either AEP overexpression or knockdown showed enhanced NRF2 activity in the nuclear or suppressed NRF2 expression in the cytoplasm of myocardial cells after irradiation, respectively, defined a possible regulatory effect of AEP associated with diminished NRF2 translocation and activation by radiation exposure, including impair myocardium and myocardial apoptosis. These findings suggest that increased levels of AEP in failing myocardium after irradiation is mediated by P53 and regulate a novel pathway that involves NRF2 activation. AEP is essential for maintaining cellular redox homeostasis of cardiac function.
Keywords: Radiation-induced myocardial injury; asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP); irradiation; nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2).
AJCR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide ameliorates radiation-induced cardiac injury.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Oct 15;11(10):6585-6599. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31737210 Free PMC article.
-
PHLPP2 downregulation protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced injury through reinforcing Nrf2/ARE antioxidant signaling.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Dec 1;314:108848. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108848. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 31610156
-
HIPK2 overexpression relieves hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis and oxidative damage of cardiomyocytes through enhancement of the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 Jan 25;316:108922. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108922. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 31837296
-
l-carnitine preserves cardiac function by activating p38 MAPK/Nrf2 signalling in hearts exposed to irradiation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Jun 5;804:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28392465
-
Asparaginyl endopeptidase induces endothelial permeability and tumor metastasis via downregulating zonula occludens protein ZO-1.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Sep 1;1865(9):2267-2275. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 May 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019. PMID: 31096007
Cited by
-
EEPD1 attenuates radiation-induced cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis by degrading FOXO3A in cardiomyocytes.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Aug 29;56(12):1733-1747. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024130. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 39210825 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Cardiac Damage Associated With Abdominal Irradiation in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 22;13:850735. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.850735. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35273513 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-223-3p Protect Against Radiation-Induced Cardiac Toxicity by Alleviating Myocardial Oxidative Stress and Programmed Cell Death via Targeting the AMPK Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 17;9:801661. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.801661. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35111759 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac exposure in left-sided breast cancer patients undergoing deep inspiratory breath hold radiation therapy.Gland Surg. 2023 May 30;12(5):677-686. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-160. Epub 2023 May 29. Gland Surg. 2023. PMID: 37284707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darby S, McGale P, Correa C, Taylor C, Arriagada R, Clarke M, Cutter D, Davies C, Ewertz M, Godwin J, Gray R, Pierce L, Whelan T, Wang Y, Peto R. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378:1707–1716. - PMC - PubMed
-
- McGale P, Taylor C, Correa C, Cutter D, Duane F, Ewertz M, Gray R, Mannu G, Peto R, Whelan T, Wang Y, Wang Z, Darby S. Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383:2127–2135. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, Vicente D, Murakami S, Hui R, Yokoi T, Chiappori A, Lee KH, de Wit M, Cho BC, Bourhaba M, Quantin X, Tokito T, Mekhail T, Planchard D, Kim YC, Karapetis CS, Hiret S, Ostoros G, Kubota K, Gray JE, Paz-Ares L, de Castro Carpeño J, Wadsworth C, Melillo G, Jiang H, Huang Y, Dennis PA, Özgüroğlu M. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1919–1929. - PubMed
-
- Xi M, Xu C, Liao Z, Chang JY, Gomez DR, Jeter M, Cox JD, Komaki R, Mehran R, Blum MA. Comparative outcomes after definitive chemoradiotherapy using proton beam therapy versus intensity modulated radiation therapy for esophageal cancer: a retrospective, single-institutional analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;99:667–676. - PubMed
-
- Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C, Elphinstone P, Evans V, Godwin J, Gray R, Hicks C, James S, MacKinnon E, McGale P, McHugh T, Peto R, Taylor C, Wang Y. Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;366:2087–2106. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
