Low miR-16 expression induces regulatory CD4+NKG2D+ T cells involved in colorectal cancer progression
- PMID: 33948372
- PMCID: PMC8085839
Low miR-16 expression induces regulatory CD4+NKG2D+ T cells involved in colorectal cancer progression
Abstract
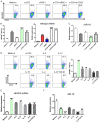
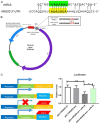
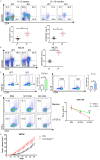
MiR-15a/16 is a member of the miRNA cluster that exhibits tumor suppression and immune modulation via targeting multiple genes. Decreased miR-15a/16 expression is involved in many cancer cells. Here, miR-16 had decreased expression in NK1.1-CD4+NKG2D+ T cells and bound with the 3'-UTR of NKG2D gene. MiR-15a/16-deficient mice had many CD4+NKG2D+ T cells, which produced TGF-β1 and IL-10 and inhibited the IFN-γ production of CD8+ T cells. Adoptive transfer of NK1.1-CD4+NKG2D+ T cells from miR-15a/16-deficient mice promoted tumor growth in vivo. However, no changes for NK1.1-CD4+NKG2D+ T cells were found in the miR-15a/16-transgenic mice. Although the miR-15a/16 transgenic mice transplanted with B16BL6 or MC38 cells exhibited rapid growth, these tumor-bearing mice did not show changes in NK1.1-CD4+NKG2D+ T cell distributions in either spleens or tumors. When NK1.1-CD4+ T cells were stimulated by α-CD3/sRAE-1 ex vivo, the NKG2D expression was difficult to induce in the T cells of miR-15a/16-transgenic mice. Finally, increased frequencies of regulatory CD4+NKG2D+ T cells with low miR-16 levels were observed in patients with late-stage colorectal cancer (Duke's C, D). Thus, miR-16 modulates NK1.1-CD4+NKG2D+ T cell functions via targeting NKG2D. Low miR-16 expression in CD4+ T cells induces the regulatory CD4+NKG2D+ T subpopulation, which promotes tumor evasion via the secretion of immune-suppressive molecules.
Keywords: CD4+ T cell; NKG2D; colorectal cancer; miR-15a/16; regulation.
AJCR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, Rassenti L, Kipps T, Negrini M, Bullrich F, Croce CM. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:15524–15529. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang E, Liu R, Chu Y. miRNA-15a/16: as tumor suppressors and more. Future Oncol. 2015;11:2351–2363. - PubMed
-
- Qian J, Jiang B, Li M, Chen J, Fang M. Prognostic significance of microRNA-16 expression in human colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 2013;37:2944–2949. - PubMed
-
- Wu WL, Wang WY, Yao WQ, Li GD. Suppressive effects of microRNA-16 on the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36:1713–1719. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
