Angiogenesis is associated with an attenuated tumor microenvironment, aggressive biology, and worse survival in gastric cancer patients
- PMID: 33948380
- PMCID: PMC8085878
Angiogenesis is associated with an attenuated tumor microenvironment, aggressive biology, and worse survival in gastric cancer patients
Abstract
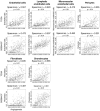
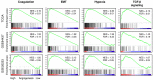
Angiogenesis is a cornerstone of cancer as it allows tumors to receive oxygen and nutrients. A high level of angiogenesis within a tumor may therefore be indicative of its aggressiveness. In this study, we examined this hypothesis in gastric cancer. Gene set variation analysis was used to measure the level of angiogenesis in tumors in 1,348 gastric cancer patients using the Hallmark_angiogenesis gene set to score tumor transcriptomes. As we predicted, there was a significant correlation between angiogenesis score and expression of angiogenesis-related genes. The score moderately correlated with abundance of vessel-related stromal cells, fibroblasts and chondrocytes in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Tumors with high score had low infiltration of T helper type 1 and 2 cells but a greater infiltration of M1 macrophages and dendritic cells. They also had enriched expression of gene sets for coagulation, hypoxia, epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and TGF-β signaling. High angiogenesis score was significantly associated with advanced AJCC stage and higher T- but not N-parameters in the TNM staging system. Patients with a high score also had shorter survival. In conclusion, bulk tumor transcriptome-based quantification of tumor angiogenesis using a computational algorithm may serve to identify patients with worse survival in gastric cancer.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; EMT; GSVA; gastric cancer; gene set; prognostic biomarker; survival.
AJCR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2020;396:635–648. - PubMed
-
- Songun I, Putter H, Kranenbarg EM, Sasako M, van de Velde CJ. Surgical treatment of gastric cancer: 15-year follow-up results of the randomised nationwide Dutch D1D2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:439–449. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
