Temporal evolution and predictors of subjective cognitive complaints up to 4 years after stroke
- PMID: 33948672
- PMCID: PMC8814883
- DOI: 10.2340/16501977-2840
Temporal evolution and predictors of subjective cognitive complaints up to 4 years after stroke
Abstract
Objective: To examine the temporal evolution of subjective cognitive complaints in the long-term after stroke, and to identify predictors of long-term subjective cognitive complaints.
Methods: Prospective cohort study including 395 stroke patients. Subjective cognitive complaints were assessed at 2 months, 6 months and 4 years post-stroke, using the Checklist for Cognitive and Emotional consequences following stroke (CLCE-24). The temporal evolution of subjective cognitive complaints was described using multilevel growth modelling. Associations between CLCE-24 cognition score at 4 years post-stroke and baseline characteristics, depression, anxiety, cognitive test performance, and adaptive and maladaptive psychological factors were examined. Significant predictors were entered in a multivariate multilevel model.
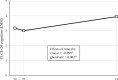
Results: A significant increase in subjective cognitive complaints from 2 months up to 4 years (mean 3.7 years, standard deviation (SD) 0.6 years) post-stroke was observed (p≤0.001). Two months post-stroke, 76% of patients reported at least one cognitive complaint, 72% at 6 months, and 89% at 4 years post-stroke. A higher level of subjective cognitive complaints at 2 months and lower scores on adaptive and maladaptive psychological factors were significant independent predictors of a higher level of subjective cognitive complaints at 4 years post-stroke.
Conclusion: Post-stroke subjective cognitive complaints increase over time and can be predicted by the extent of subjective cognitive complaints and the presence of adaptive and maladaptive psychological factors in the early phases after stroke.
Keywords: cognition; cognitive complaints; rehabilitation; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Course and Predictors of Subjective Cognitive Complaints During the First 12 Months after Stroke.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 Mar;29(3):104588. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.104588. Epub 2020 Jan 9. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 31926677
-
Psychological factors are associated with subjective cognitive complaints 2 months post-stroke.Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2017 Jan;27(1):99-115. doi: 10.1080/09602011.2015.1065280. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2017. PMID: 26207868
-
Psychological factors and subjective cognitive complaints after stroke: Beyond depression and anxiety.Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2019 Dec;29(10):1671-1684. doi: 10.1080/09602011.2018.1441720. Epub 2018 Mar 4. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 29502474
-
Prevalence and Profile of Poststroke Subjective Cognitive Complaints.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015 Aug;24(8):1823-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.04.017. Epub 2015 May 18. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25997979
-
Cognition, Emotion and Fatigue Post-stroke.2021 Jan 15. In: Platz T, editor. Clinical Pathways in Stroke Rehabilitation: Evidence-based Clinical Practice Recommendations [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2021. 2021 Jan 15. In: Platz T, editor. Clinical Pathways in Stroke Rehabilitation: Evidence-based Clinical Practice Recommendations [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2021. PMID: 36315696 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Randomised control trial of virtual reality in cognitive rehabilitation: effectiveness and near-transfer effect for stroke patients.BMC Psychol. 2025 Jul 18;13(1):805. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-03135-8. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40682194 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cognitive recovery in patients with post-stroke subjective cognitive complaints.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 27;13:977641. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.977641. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36237629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pendlebury ST, Mariz J, Bull L, Mehta Z, Rothwell PM. MoCA, ACE-R, and MMSE versus the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Canadian Stroke Network Vascular Cognitive Impairment Harmonization Standards Neuropsychological Battery after TIA and stroke. Stroke 2012; 43: 464–469. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lamb F, Anderson J, Saling M, Dewey H. Predictors of subjective cognitive complaint in postacute older adult stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2013; 94: 1747–1752. - PubMed
-
- van Rijsbergen MW, Mark RE, de Kort PL, Sitskoorn MM. Subjective cognitive complaints after stroke: a systematic review. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2014; 23: 408–420. - PubMed
-
- Duits A, Munnecom T, van Heugten C, van Oostenbrugge RJ. Cognitive complaints in the early phase after stroke are not indicative of cognitive impairment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2008; 79: 143–146. - PubMed
-
- Narasimhalu K, Wiryasaputra L, Sitoh Y, Kandiah N. Post-stroke subjective cognitive impairment is associated with acute lacunar infarcts in the basal ganglia. Eur J Neurol 2013; 20: 547–551. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

