Impact of anti-thymocyte globulin dose for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation from matched unrelated donors: a multicenter experience
- PMID: 33948721
- PMCID: PMC8195753
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-021-04521-z
Impact of anti-thymocyte globulin dose for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation from matched unrelated donors: a multicenter experience
Abstract
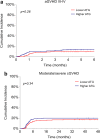
Despite the widespread use of rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG) to prevent acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD, cGVHD) after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT), convincing evidence about an optimal dose is lacking. We retrospectively evaluated the clinical impact of two different ATG doses (5 vs 6-7.5 mg/kg) in 395 adult patients undergoing HSCT from matched unrelated donors (MUD) at 3 Italian centers. Cumulative incidence of aGVHD and moderate-severe cGVHD did not differ in the 2 groups. We observed a trend toward prolonged overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) with lower ATG dose (5-year OS and DFS 56.6% vs. 46.3%, p=0.052, and 46.8% vs. 38.6%, p=0.051, respectively) and no differences in relapse incidence and non-relapse mortality. However, a significantly increased infection-related mortality (IRM) was observed in patients who received a higher ATG dose (16.7% vs. 8.8% in the lower ATG group, p=0.019). Besides, graft and relapse-free survival (GRFS) was superior in the lower ATG group (5-year GRFS 43.1% vs. 32.4%, p=0.014). The negative impact of higher ATG dose on IRM and GRFS was confirmed by multivariate analysis. Our results suggest that ATG doses higher than 5 mg/kg are not required for MUD allo-HCT and seem associated with worse outcomes.
Keywords: Anti-thymocyte globulin; GvHD; Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Matched unrelated donors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lee SJ, Klein J, Haagenson M, Baxter-Lowe LA, Confer DL, Eapen M, Fernandez-Vina M, Flomenberg N, Horowitz M, Hurley CK, Noreen H, Oudshoorn M, Petersdorf E, Setterholm M, Spellman S, Weisdorf D, Williams TM, Anasetti C. High-resolution donor-recipient HLA matching contributes to the success of unrelated donor marrow transplantation. Blood. 2007;110:4576–4583. - PubMed
-
- Storb R, Deeg HJ, Farewell V, Doney K, Appelbaum F, Beatty P, Bensinger W, Buckner CD, Clift R, Hansen J. Marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: methotrexate alone compared with a combination of methotrexate and cyclosporine for prevention of acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 1986;68:119–125. - PubMed
-
- Ringdén O, Klaesson S, Sundberg B, Ljungman P, Lönnqvist B, Persson U. Decreased incidence of graft-versus-host disease and improved survival with methotrexate combined with cyclosporin compared with monotherapy in recipients of bone marrow from donors other than HLA identical siblings. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1992;9:19–25. - PubMed
-
- Nash RA, Johnston L, Parker P, McCune JS, Storer B, Slattery JT, Furlong T, Anasetti C, Appelbaum FR, Lloid ME, Deeg HJ, Kiem HP, Martin PJ, Schubert MM, Witherspoon RP, Forman SJ, Blume KG, Storb R. A phase I/II study of mycophenolate mofetil in combination with cyclosporine for prophylaxis of acute graft-versus-host disease after myeloablative conditioning and allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005;11:495–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

