Tumor necrosis factor-induced ArhGEF10 selectively activates RhoB contributing to human microvascular endothelial cell tight junction disruption
- PMID: 33948992
- PMCID: PMC9026622
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202002783RR
Tumor necrosis factor-induced ArhGEF10 selectively activates RhoB contributing to human microvascular endothelial cell tight junction disruption
Abstract
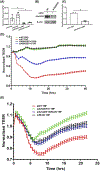
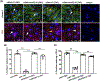
Capillary endothelial cells (ECs) maintain a semi-permeable barrier between the blood and tissue by forming inter-EC tight junctions (TJs), regulating selective transport of fluid and solutes. Overwhelming inflammation, as occurs in sepsis, disrupts these TJs, leading to leakage of fluid, proteins, and small molecules into the tissues. Mechanistically, disruption of capillary barrier function is mediated by small Rho-GTPases, such as RhoA, -B, and -C, which are activated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and disrupted by GTPase-activating factors (GAPs). We previously reported that a mutation in a specific RhoB GAP (p190BRhoGAP) underlays a hereditary capillary leak syndrome. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) treatment disrupts TJs in cultured human microvascular ECs, a model of capillary leak. This response requires new gene transcription and involves increased RhoB activation. However, the specific GEF that activates RhoB in capillary ECs remains unknown. Transcriptional profiling of cultured tight junction-forming human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMECs) revealed that 17 GEFs were significantly induced by TNF. The function of each candidate GEF was assessed by short interfering RNA depletion and trans-endothelial electrical resistance screening. Knockown of ArhGEF10 reduced the TNF-induced loss of barrier which was phenocopied by RhoB or dual ArhGEF10/RhoB knockdown. ArhGEF10 knockdown also reduced the extent of TNF-induced RhoB activation and disruption at tight junctions. In a cell-free assay, immunoisolated ArhGEF10 selectively catalyzed nucleotide exchange to activate RhoB, but not RhoA or RhoC. We conclude ArhGEF10 is a TNF-induced RhoB-selective GEF that mediates TJ disruption and barrier loss in human capillary endothelial cells.
Keywords: Rho guanine nucleotide-exchange factor; capillary leak; inflammation; permeability; transendothelial electrical resistance; vascular dysfunction.
© 2021 Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No authors have any relevant disclosures.
Figures

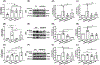
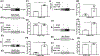
Similar articles
-
ArhGEF12 activates Rap1A and not RhoA in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells to reduce tumor necrosis factor-induced leak.FASEB J. 2022 Apr;36(4):e22254. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101873RR. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35294066 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor disrupts claudin-5 endothelial tight junction barriers in two distinct NF-κB-dependent phases.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 27;10(3):e0120075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120075. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25816133 Free PMC article.
-
A p190BRhoGAP mutation and prolonged RhoB activation in fatal systemic capillary leak syndrome.J Exp Med. 2017 Dec 4;214(12):3497-3505. doi: 10.1084/jem.20162143. Epub 2017 Nov 2. J Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 29097442 Free PMC article.
-
A current overview of RhoA, RhoB, and RhoC functions in vascular biology and pathology.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Dec;206:115321. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115321. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36306821 Review.
-
Regulation and functions of the RhoA regulatory guanine nucleotide exchange factor GEF-H1.Small GTPases. 2021 Sep-Nov;12(5-6):358-371. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2020.1840889. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 33126816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long Noncoding RNA FBXL19-AS1-Mediated Ulcerative Colitis-Associated Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Defect.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022 Oct;19(5):1077-1088. doi: 10.1007/s13770-022-00479-9. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022. PMID: 36048401 Free PMC article.
-
ArhGEF12 activates Rap1A and not RhoA in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells to reduce tumor necrosis factor-induced leak.FASEB J. 2022 Apr;36(4):e22254. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101873RR. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35294066 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic profiles integrated with transcriptomic reveal the difference between COPD and PRISm in KOCOSS-NIH.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Apr 10;25(1):86. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01593-2. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40205238 Free PMC article.
-
Blood‑brain barrier dysfunction in epilepsy: Mechanisms, therapeutic strategies and future orientation (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Sep;56(3):136. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5577. Epub 2025 Jul 4. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40613229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PCDH7 as the key gene related to the co-occurrence of sarcopenia and osteoporosis.Front Genet. 2023 Jul 5;14:1163162. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1163162. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37476411 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

