Hopelessness and Depression Predict Sarcopenia in Advanced CKD and Dialysis: A Multicenter Cohort Study
- PMID: 33949624
- PMCID: PMC12280643
- DOI: 10.1007/s12603-020-1556-4
Hopelessness and Depression Predict Sarcopenia in Advanced CKD and Dialysis: A Multicenter Cohort Study
Abstract
Background/objectives: Depression and hopelessness are frequently experienced in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and are generally associated with lessened physical activity. The aim of this study was to quantify the associations between sarcopenia as determined by SARC-F with both depression and hopelessness.
Design and setting: This multicenter cohort study involving cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses was conducted in a university hospital and four general hospitals, each with a nephrology center, in Japan.
Participants: Participants consisted of 314 CKD patients (mean age 67.6), some of whom were receiving dialysis (228, 73%).
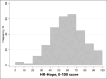
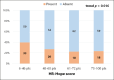
Measurements: The main exposures were depression, measured using the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D) questionnaire, and hopelessness, measured using a recently developed 18-item health-related hope scale (HR-Hope). The outcomes were sarcopenia at baseline and one year after, measured using the SARC-F questionnaire. Logistic regression models were applied.
Results: The cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses included 314 and 180 patients, respectively. Eighty-nine (28.3%) patients experienced sarcopenia at baseline, and 44 (24.4%) had sarcopenia at the one-year follow-up. More hopelessness (per 10-point lower, adjusted odds ratio [AOR]: 1.33, 95% confidence interval [95% CI] 1.12-1.58), depression (AOR: 1.87, 95% CI 1.003-3.49), age (per 10-year higher, AOR: 1.70, 95% CI 1.29-2.25), being female (AOR: 2.67, 95% CI 1.43-4.98), and undergoing hemodialysis (AOR, 2.92; 95% CI, 1.41-6.05) were associated with a higher likelihood of having baseline sarcopenia. More hopelessness (per 10-point lower, AOR: 1.69, 95% CI 1.14-2.51) and depression (AOR: 4.64, 95% CI: 1.33-16.2) were associated with a higher likelihood of having sarcopenia after one year.
Conclusions: Among patients with different stages of CKD, both hopelessness and depression predicted sarcopenia. Provision of antidepressant therapies or goal-oriented educational programs to alleviate depression or hopelessness can be useful options to prevent sarcopenia.
Keywords: Depression; chronic kidney disease; health-related hope; hopelessness; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyere O, Cederholm T, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16–31. 10.1093/ageing/afy169 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lamarca F, Carrero JJ, Rodrigues JC, Bigogno FG, Fetter RL, Avesani CM. Prevalence of sarcopenia in elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients: the impact of different diagnostic criteria. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014;18(7):710–717. 10.1007/s12603-014-0505-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pereira RA, Cordeiro AC, Avesani CM, Carrero JJ, Lindholm B, Amparo FC, et al. Sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease on conservative therapy: prevalence and association with mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30(10):1718–1725. 10.1093/ndt/gfv133 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Giglio J, Kamimura MA, Lamarca F, Rodrigues J, Santin F, Avesani CM. Association of sarcopenia with nutritional parameters, quality of life, hospitalization, and mortality rates of elderly patients on hemodialysis. J Ren Nutr. 2018;28(3):197–207. 10.1053/j.jrn.2017.12.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang KV, Hsu TH, Wu WT, Huang KC, Han DS. Is sarcopenia associated with depression? A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Age Ageing. 2017;46(5):738–746. 10.1093/ageing/afx094 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

