Association between interleukin-1 alpha rs1800587 polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 33950757
- PMCID: PMC10455026
- DOI: 10.1177/00368504211013647
Association between interleukin-1 alpha rs1800587 polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis
Abstract
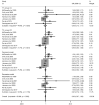
No consistent results have been reached on the relationship of interleukin-1 (IL-1) rs1800587 polymorphism with the susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) so far. Therefore, the current meta-analysis was designed to thoroughly review relevant studies, in order to examine the relationship of IL-1A rs1800587 polymorphism with RA risk. Electronic databases were retrieved for literature regarding the relationship between IL-1A rs1800587 polymorphism and RA vulnerability according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Stata 12.0 software was adopted to examine the enrolled literature. Meanwhile, odds ratio (OR) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were used to evaluate the association. A total of seven case-control researches (3267 patients and 2960 healthy controls) were eventually enrolled into the current meta-analysis. Our data indicated no correlation of IL-1A rs1800587 polymorphism with RA risk (TT vs CC: OR = 0.90, 95% CI = 0.73-1.11; TC vs CC: OR = 1.02, 95% CI = 0.78-1.34; Dominant model: OR = 1.04, 95% CI = 0.80-1.35; Recessive model: OR = 1.91, 95% CI = 0.74-1.12). Similarly, no association was found in subgroup analysis stratified by ethnicity. Our findings indicated no relationship between IL-1A rs1800587 polymorphism and RA vulnerability.
Keywords: IL-1 polymorphism; Rheumatoid arthritis; risk.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association between IL-1A (-889C/T) polymorphism and susceptibility of chronic periodontitis: A meta-analysis.Gene. 2020 Mar 1;729:144227. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144227. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Gene. 2020. PMID: 31759990
-
Associations between interleukin-1 and IL-1 receptor antagonist polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2015 Dec 26;61(8):105-11. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2015. PMID: 26718437
-
Meta-analyses of IL1A polymorphisms and the risk of several autoimmune diseases published in databases.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 7;13(6):e0198693. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198693. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29879187 Free PMC article.
-
Association of interleukin-1 family cytokines single nucleotide polymorphisms with susceptibility to systemic sclerosis: an independent case-control study and a meta-analysis.Immunol Res. 2016 Aug;64(4):1041-52. doi: 10.1007/s12026-016-8797-7. Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27098064
-
Interleukin-6-174G > C (rs1800795) polymorphism distribution and its association with rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study and meta-analysis.Autoimmunity. 2017 May;50(3):158-169. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2016.1261833. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Autoimmunity. 2017. PMID: 28010120
References
-
- Trouw LA, Pickering MC, Blom AM. The complement system as a potential therapeutic target in rheumatic disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2017; 13: 538–547. - PubMed
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003; 423: 356–361. - PubMed
-
- Xue J, Mou L, Lu X, et al. No association of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist VNTR polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility: a meta analysis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2010; 28: 654–660. - PubMed
-
- Bresnihan B, Cobby M. Clinical and radiological effects of anakinra in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003; 42: ii22–ii28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

