Axial length targets for myopia control
- PMID: 33951213
- PMCID: PMC8252804
- DOI: 10.1111/opo.12812
Axial length targets for myopia control
Abstract
Purpose: Both emmetropic and myopic eyes elongate throughout childhood. The goals of this study were to compare axial elongation among untreated progressing myopes, progressing myopes treated with a myopia control contact lens and emmetropes, in order to place axial elongation in the context of normal eye growth in emmetropic children, and to consider whether normal physiological eye growth places limits on what might be achieved with myopia control.
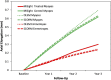
Methods: Axial elongation data were taken from the 3-year randomised clinical trial of a myopia control dual-focus (MiSight® 1 day) contact lens. These were compared with data for myopic and emmetropic children in two large cohort studies: the Orinda Longitudinal Study of Myopia (OLSM) and the Singapore Cohort Study of the Risk Factors for Myopia (SCORM). Each study's published equations were used to calculate annual axial elongation. Four virtual cohorts-myopic and emmetropic for each model-were created, each with the same age distribution as the MiSight clinical trial subjects and the predicted cumulative elongation calculated at years 1, 2 and 3 for myopes and emmetropes using both the OLSM and SCORM models.
Results: The untreated control myopes in the MiSight clinical trial showed mean axial elongation over 3 years (0.62 mm) similar to the virtual cohorts based on the OLSM (0.70 mm) and SCORM (0.65 mm) models. The predicted 3-year axial elongation for the virtual cohorts of emmetropes was 0.24 mm for both the OLSM and SCORM models-similar to the mean 3-year elongation in MiSight-treated myopes (0.30 mm).
Conclusions: The 3-year elongation in MiSight-treated myopes approached that of virtual cohorts of emmetropes with the same age distribution. It is hypothesised that myopic axial elongation is superimposed on an underlying physiological axial elongation observed in emmetropic eyes, which reflects increases in body stature. We speculate that optically based myopia control treatments may minimise the myopic axial elongation but retain the underlying physiological elongation observed in emmetropic eyes.
Keywords: axial length; children; contact lenses; myopia; myopia control.
© 2021 The Authors. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of College of Optometrists.
Conflict of interest statement
Paul Chamberlain, Percy Lazon and Baskar Arumugam are employees of CooperVision. Mark Bullimore is a consultant for Alcon Research, Inc., Apellis, Inc., Arctic Vision, Inc., Ascpleix, Inc., CooperVision, Inc., Corneagen, Inc., Essilor International S.A.., Eyenovia, Inc., Genentech, Inc., Johnson & Johnson Vision, Inc., Presbia, Inc., and is the sole owner of Ridgevue Publishing, LLC, Ridgevue Technologies LLC, and Ridgevue Vision LLC. Preparation of this paper was supported by CooperVision, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Normative data for emmetropic and myopic eye growth in childhood.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2021 Nov;41(6):1382-1383. doi: 10.1111/opo.12873. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2021. PMID: 34402539 No abstract available.
-
Author's reply.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2021 Nov;41(6):1384. doi: 10.1111/opo.12872. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2021. PMID: 34402540 No abstract available.
References
-
- Grosvenor T & Goss DA. Role of the cornea in emmetropia and myopia. Optom Vis Sci 1998; 75: 132–145. - PubMed
-
- Grosvenor T & Scott R. Role of the axial length/corneal radius ratio in determining the refractive state of the eye. [See Comments] Optom Vis Sci 1994; 71: 573–579. - PubMed
-
- Rozema JJ, Atchison DA & Tassignon MJ. Comparing methods to estimate the human lens power. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011; 52: 7937–7942. - PubMed
-
- Cruickshank FE & Logan NS. Optical 'Dampening' of the refractive error to axial length ratio: implications for outcome measures in myopia control studies. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2018; 38: 290–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

