Pharmacological Wnt ligand inhibition overcomes key tumor-mediated resistance pathways to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy
- PMID: 33951424
- PMCID: PMC8148423
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109071
Pharmacological Wnt ligand inhibition overcomes key tumor-mediated resistance pathways to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy
Abstract
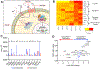
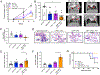
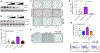
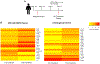
While immune checkpoint blockade is associated with prolonged responses in multiple cancers, most patients still do not benefit from this therapeutic strategy. The Wnt-β-catenin pathway is associated with diminished T cell infiltration; however, activating mutations are rare, implicating a role for autocrine/paracrine Wnt ligand-driven signaling in immune evasion. In this study, we show that proximal mediators of the Wnt signaling pathway are associated with anti-PD-1 resistance, and pharmacologic inhibition of Wnt ligand signaling supports anti-PD-1 efficacy by reversing dendritic cell tolerization and the recruitment of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells in autochthonous tumor models. We further demonstrate that the inhibition of Wnt signaling promotes the development of a tumor microenvironment that is more conducive to favorable responses to checkpoint blockade in cancer patients. These findings support a rationale for Wnt ligand-focused treatment approaches in future immunotherapy clinical trials and suggest a strategy for selecting those tumors more responsive to Wnt inhibition.
Keywords: Wnt inhibition; Wnt-β-catenin pathway; anti-PD-1 resistance; dendritic cells; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; melanoma; myeloid-deriver suppressor cells; non-small cell lung cancer; regulatory T cells; tumor immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.K.S. received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Immunocore, and Merck. J.H.S. received research funding from A(∗)STAR Singapore, Curegenix, and Leap. J.H.S. has also received research funding and served on the scientific advisory board for OncoMed. B.A.H. received research funding from OncoMed, Merck, and Leap. B.A.H., N.C.D., and B.T. are authors on a patent describing paracrine Wnt ligand signaling as a predictive marker for cancer immunotherapy. V.N.D. is an employee of EDDC/A(∗)STAR and is an author on a patent on combining ETC-159 with pembrolizumab. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bagby SM, Hartman SJ, Navarro NM, Yacob BW, Shulman J, Barkow J, Lieu CH, Davis SL, Leal AD, Messersmith WA, et al. (2020). Sensitizing microsatellite stable colorectal cancer to immune checkpoint therapy utilizing Wnt pathway inhibition. Cancer Res. 80 (16, Suppl), 6647. https://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/80/16_Supplement/6647.
-
- Clevers H, and Nusse R (2012). Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 149, 1192–1205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

