KIM-1 mediates fatty acid uptake by renal tubular cells to promote progressive diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 33951465
- PMCID: PMC8132466
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.04.004
KIM-1 mediates fatty acid uptake by renal tubular cells to promote progressive diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
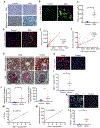
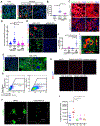
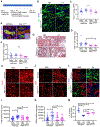
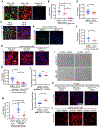
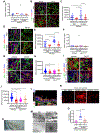
Tubulointerstitial abnormalities are predictive of the progression of diabetic kidney disease (DKD), and their targeting may be an effective means for prevention. Proximal tubular (PT) expression of kidney injury molecule (KIM)-1, as well as blood and urinary levels, are increased early in human diabetes and can predict the rate of disease progression. Here, we report that KIM-1 mediates PT uptake of palmitic acid (PA)-bound albumin, leading to enhanced tubule injury with DNA damage, PT cell-cycle arrest, interstitial inflammation and fibrosis, and secondary glomerulosclerosis. Such injury can be ameliorated by genetic ablation of the KIM-1 mucin domain in a high-fat-fed streptozotocin mouse model of DKD. We also identified TW-37 as a small molecule inhibitor of KIM-1-mediated PA-albumin uptake and showed in vivo in a kidney injury model in mice that it ameliorates renal inflammation and fibrosis. Together, our findings support KIM-1 as a new therapeutic target for DKD.
Keywords: DNA damage response; HAVCR1; TIM-1; albuminuria; chronic kidney disease; diabetic nephropathy; proximal tubule; renal fibrosis; senescence; tubulointerstitial disease.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.V.B. and T.I. are co-inventors on KIM-1 patents assigned to Mass General Brigham. J.V.B. and A.K.A. have filed a patent for the discovery of TW-37 as inhibitor of KIM-1 to alleviate chronic kidney disease. J.V.B. is a consultant to Cadent, Praxis, Seattle Genetics, Aldeyra, Sarepta, Praxis, and Angion and owns equity in Goldfinch, Innoviva, MediBeacon, DxNow, Verinano, Autonomous Medical Devices, Renalytix, Pacific Biosciences, and Sentien. V.K.K. has an ownership interest in Tizona Therapeutics, Celsius Therapeutics, and Bicara Therapeutics. V.K.K. has financial interests in Biocon Biologic, BioLegend, Elpiscience Biopharmaceutical Ltd., Equilium Inc., and Syngene Intl. V.K.K. is a member of SABs for Elpiscience Biopharmaceutical Ltd., GSK, Rubius Therapeutics, and Tizona Therapeutics. J.V.B.’s and V.K.K.’s interests were reviewed and are managed by Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Mass General Brigham in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies. S.X. is an employee and shareholder of Celsius Therapeutics. J.H. is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. TW-37 was identified as a KIM-1 inhibitor in a screen supported by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham RT (2001). Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev 15, 2177–2196. - PubMed
-
- Akazawa Y, Nakashima R, Matsuda K, Okamaoto K, Hirano R, Kawasaki H, Miuma S, Miyaaki H, Malhi H, Abiru S, et al. (2019). Detection of DNA damage response in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via p53-binding protein 1 nuclear expression. Mod Pathol 32, 997–1007. - PubMed
-
- Arici M, Chana R, Lewington A, Brown J, and Brunskill NJ (2003). Stimulation of proximal tubular cell apoptosis by albumin-bound fatty acids mediated by peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma. J Am Soc Nephrol 14, 17–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

