Immunological and inflammatory profiles during acute and convalescent phases of severe/ critically ill COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 33951560
- PMCID: PMC8052478
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107685
Immunological and inflammatory profiles during acute and convalescent phases of severe/ critically ill COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Background: The 2019 Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic poses a huge threat internationally; however, the role of the host immune system in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 is not well understood.
Methods: Cytokine and chemokine levels and characterisation of immune cell subsets from 20 COVID-19 cases after hospital admission (17 critically ill and 3 severe patients) and 16 convalescent patients were determined using a multiplex immunoassay and flow cytometry, respectively.
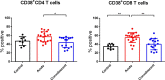
Results: IP-10, MCP-1, MIG, IL-6, and IL-10 levels were significantly higher in acute severe/critically ill patients with COVID-19, whereas were normal in patients who had reached convalescence. CD8 T cells in severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients expressed high levels of cytotoxic granules (granzyme B and perforin)and was hyperactivated as evidenced by the high proportions of CD38. Furthermore, the cytotoxic potential of natural killer (NK) cells, and the frequencies of myeloid dendritic cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells was reduced in patients with severe and critical COVID-19; however, these dysregulations were found to be restored in convalescent phases.
Conclusion: Thus, elicitation of the hyperactive cytokine-mediated inflammatory response, dysregulation of CD8 T and NK cells, and deficiency of host myeloid and plasmacytoid DCs, may contribute to COVID-19 pathogenesis and provide insights into potential therapeutic targets and strategies.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytokines /chemokines; Immune cell; Severe/critical infection.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Wu F., Zhao S., Yu B., Chen Y.M., Wang W., Song Z.G., Hu Y., Tao Z.W., Tian J.H., Pei Y.Y., Yuan M.L., Zhang Y.L., Dai F.H., Liu Y., Wang Q.M., Zheng J.J., Xu L., Holmes E.C., Zhang Y.Z. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature. 2020;579(7798):265–269. - PMC - PubMed
-
- N. Zhu, D. Zhang, W. Wang, X. Li, B. Yang, J. Song, X. Zhao, B. Huang, W. Shi, R. Lu, P. Niu, F. Zhan, X. Ma, D. Wang, W. Xu, G. Wu, G.F. Gao, W. Tan, I. China Novel Coronavirus, T. Research, A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med 382(8) (2020) 727-733. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu R., Zhao X., Li J., Niu P., Yang B., Wu H., Wang W., Song H., Huang B., Zhu N., Bi Y., Ma X., Zhan F., Wang L., Hu T., Zhou H., Hu Z., Zhou W., Zhao L., Chen J., Meng Y., Wang J., Lin Y., Yuan J., Xie Z., Ma J., Liu W.J., Wang D., Xu W., Holmes E.C., Gao G.F., Wu G., Chen W., Shi W., Tan W. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. The Lancet. 2020;395(10224):565–574. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., Ren L., Zhao J., Hu Y., Zhang L., Fan G., Xu J., Gu X., Cheng Z., Yu T., Xia J., Wei Y., Wu W., Xie X., Yin W., Li H., Liu M., Xiao Y., Gao H., Guo L., Xie J., Wang G., Jiang R., Gao Z., Jin Q., Wang J., Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China, The Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., Guan L., Wei Y., Li H., Wu X., Xu J., Tu S., Zhang Y., Chen H., Cao B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. The Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054–1062. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

