Impaired inhibitory GABAergic synaptic transmission and transcription studied in single neurons by Patch-seq in Huntington's disease
- PMID: 33952696
- PMCID: PMC8126788
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2020293118
Impaired inhibitory GABAergic synaptic transmission and transcription studied in single neurons by Patch-seq in Huntington's disease
Abstract
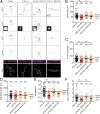
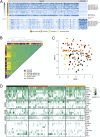
Transcriptional dysregulation in Huntington's disease (HD) causes functional deficits in striatal neurons. Here, we performed Patch-sequencing (Patch-seq) in an in vitro HD model to investigate the effects of mutant Huntingtin (Htt) on synaptic transmission and gene transcription in single striatal neurons. We found that expression of mutant Htt decreased the synaptic output of striatal neurons in a cell autonomous fashion and identified a number of genes whose dysregulation was correlated with physiological deficiencies in mutant Htt neurons. In support of a pivotal role for epigenetic mechanisms in HD pathophysiology, we found that inhibiting histone deacetylase 1/3 activities rectified several functional and morphological deficits and alleviated the aberrant transcriptional profiles in mutant Htt neurons. With this study, we demonstrate that Patch-seq technology can be applied both to better understand molecular mechanisms underlying a complex neurological disease at the single-cell level and to provide a platform for screening for therapeutics for the disease.
Keywords: Huntington’s disease; Patch-seq; single-cell RNA sequencing; striatum; synaptic function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures





References
-
- Vonsattel J. P., DiFiglia M., Huntington disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 57, 369–384 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Graveland G. A., DiFiglia M., The frequency and distribution of medium-sized neurons with indented nuclei in the primate and rodent neostriatum. Brain Res. 327, 307–311 (1985). - PubMed
-
- Kemp J. M., Powell T. P. S., The structure of the caudate nucleus of the cat: Light and electron microscopy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 262, 383–401 (1971). - PubMed
-
- The Huntington’s Disease Collaborative Research Group , A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosomes. Cell 72, 971–983 (1993). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

