PONDx: real-life utilization and decision impact of the 21-gene assay on clinical practice in Italy
- PMID: 33953182
- PMCID: PMC8099872
- DOI: 10.1038/s41523-021-00246-4
PONDx: real-life utilization and decision impact of the 21-gene assay on clinical practice in Italy
Abstract
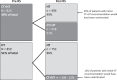
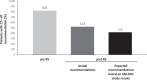
Clinicopathological prognostic features have limited value to identify with precision newly diagnosed patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer (BC), who would benefit from chemotherapy (CT) in addition to adjuvant hormonal therapy (HT). The 21-gene Oncotype DX Breast Recurrence Score® (RS) assay has been demonstrated to predict CT benefit, hence supporting personalized decisions on adjuvant CT. The multicenter, prospective, observational study PONDx investigated the real-life use of RS® results in Italy and its impact on treatment decisions. Physicians' treatment recommendations (HT ± CT) were documented before and after availability of RS results, and changes in recommendations were determined. In the HR+ HER2- early BC population studied (N = 1738), physicians recommended CT + HT in 49% of patients pre-RS. RS-guided treatment decisions resulted in 36% reduction of CT recommendations. PONDx confirms that RS results provide clinically relevant information for CT recommendation in early-stage BC, resulting in a reduction of more than a third of CT use.
Conflict of interest statement
F.C.: Genomic Health, Inc., Roche, Eli Lilly, Bayer, Novartis, Amgen, Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Eisai, Merch-Serono, Boheringer Ingelheim, MSD, BMS, Takeda, Astellas Oncology, Abbott. S.B.: Genomic Health, Inc. A.F.: Roche, Celgene, Astra Zeneca, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Eisai. M.G.: Roche, Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Celgene, Eli, Lilly, Amgen, and Eisai. M.C.: Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Pfizer, OBI Pharma, Puma Biotechnology, Celldex, Astra zeneca. A.Z.: Roche, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer. D.G.: Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Eisai. D.A.: Genomic Health, Inc. G.N.: Pfizer, Genomic Health, Inc., Italfarmaco. P.V.: Eisai, Roche, Pfizer, Novartis, Gentili. D.C.: Novartis, Roche. G.B.: Eli Lilly, Novartis. G.T.: Novartis Pfizer Italfarmaco e Molteni. T.G.: Novartis Roche Celgine Pfeizer Lilly Gentili. G.C., R.M., D.F., A.R., P.S., F.S., L. Vigna, C.T., D.S., M.A.F., E.M., G.S., G.P., A.F.S., R.B., and L. Vassalli declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG et al. Comparisons between different polychemotherapy regimens for early breast cancer: meta-analyses of long-term outcome among 100,000 women in 123 randomised trials. Lancet. 2012;379:432–444. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61625-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

